Android SO 文件加载过程
一、前言
针对 Android so 文件加载过程只有一个很浅显的认识,后来想稍微系统学习的时候,AOSP 的源码不公开了…直到最近在看雪上看到一篇文章,里面贴出了一个网址,可以正常访问到 AOSP 的源码,于是乎打算学习并记录一下。
二、开始
在 Android 中,.so 文件是 共享库 文件,共享库文件又可以细分为 动态链接库(动态 .so 文件)和 静态链接库(静态 .a 文件)。但在 Android 中一般更常见的是动态 .so 文件,静态链接库通常在编译时就被集成到最终应用中,而不是直接加载。所以经常看到的 so 文件的链接大多都是以动态链接的。
动态链接会利用对应的打包生成的 APK,按照对应的 ABI(lib/armeabi-v7a/,lib/arm64-v8a/,lib/x86/,lib/x86_64/)去选择对应的 so 文件,然后去实现在 Java 层的调用,或者在 native 层调用 Java层的代码逻辑。
Java 代码使用 静态 System.loadLibrary("libsofile") 来加载共享库文件;或者通过动态加载路径的 so 文件来实现。
在 Android 中,静态链接库 (.a 文件)是被链接到最终的可执行文件中,而不是在运行时加载。Android NDK 编译时,静态库会被打包到 APK 中的应用代码部分。
要探究 so 文件最真实的加载过程就从 System.load(soPath); 开始,去剖析安卓源码。
这里我就用自己写的一个题目为例,来进行分析。首先看到在 MainActivity.java 中的 System.loadLibrary(“ctf1”);。
跟进 loadLibrary 函数
@CallerSensitive
public static void loadLibrary(String libname) {
Runtime.getRuntime().loadLibrary0(Reflection.getCallerClass(), libname);
}
首先第一行的注解,作用是告诉 JVM/安全检查逻辑:
- 这个方法的行为 依赖于调用者是谁;
- 不能随便内联或优化,因为它需要直到调用栈上是谁在调用。
比如 System.loadLibrary 最终要决定:是允许调用方加载本地库,还是拒绝(比如安全管理器里限制);所以 JVM 会特别处理 @CallerSensitive,正确识别“真实的调用者类”。
接下来通过 Java 的反射机制拿到调用类,并和 so 文件名一起传入到由 JVM 的运行时对象调用的 loadLibrary0 方法中。到这里要想再进一步跟进就得上网站看 Android 源码了。直接进行搜索,就可以找到。

该方法先拿到调用者类对应的类加载器,然后又将其作为参数之一,调用了另一个重载版本,继续跟进。
private synchronized void loadLibrary0(ClassLoader loader, Class<?> callerClass, String libname) {
if (libname.indexOf((int)File.separatorChar) != -1) {
throw new UnsatisfiedLinkError(
"Directory separator should not appear in library name: " + libname);
}
String libraryName = libname;
// Android-note: BootClassLoader doesn't implement findLibrary(). http://b/111850480
// Android's class.getClassLoader() can return BootClassLoader where the RI would
// have returned null; therefore we treat BootClassLoader the same as null here.
if (loader != null && !(loader instanceof BootClassLoader)) {
String filename = loader.findLibrary(libraryName);
if (filename == null &&
(loader.getClass() == PathClassLoader.class ||
loader.getClass() == DelegateLastClassLoader.class)) {
// Don't give up even if we failed to find the library in the native lib paths.
// The underlying dynamic linker might be able to find the lib in one of the linker
// namespaces associated with the current linker namespace. In order to give the
// dynamic linker a chance, proceed to load the library with its soname, which
// is the fileName.
// Note that we do this only for PathClassLoader and DelegateLastClassLoader to
// minimize the scope of this behavioral change as much as possible, which might
// cause problem like b/143649498. These two class loaders are the only
// platform-provided class loaders that can load apps. See the classLoader attribute
// of the application tag in app manifest.
filename = System.mapLibraryName(libraryName);
}
if (filename == null) {
// It's not necessarily true that the ClassLoader used
// System.mapLibraryName, but the default setup does, and it's
// misleading to say we didn't find "libMyLibrary.so" when we
// actually searched for "liblibMyLibrary.so.so".
throw new UnsatisfiedLinkError(loader + " couldn't find \"" +
System.mapLibraryName(libraryName) + "\"");
}
String error = nativeLoad(filename, loader, callerClass);
if (error != null) {
throw new UnsatisfiedLinkError(error);
}
return;
}
// We know some apps use mLibPaths directly, potentially assuming it's not null.
// Initialize it here to make sure apps see a non-null value.
getLibPaths();
String filename = System.mapLibraryName(libraryName);
String error = nativeLoad(filename, loader, callerClass);
if (error != null) {
throw new UnsatisfiedLinkError(error);
}
}
该重载方法首先先检查库名是否合法,然后判断 loader 非空且不是 BootClassLoader,就调用 findLibrary,让类加载器自己找库文件;而如果找不到,就会分别调用 PathClassLoader 和 DelegateLastClassLoader 再进一步尝试去加载库。如果依旧找不到,那么系统就会抛出 UnsatisfiedLinkError,告诉开发人员哪个 ClassLoader 找不到哪个库。接下来便是调用 JNI 层方法 nativeLoad,内部最终会调用 dlopen 函数。而如果 loader 为 null 或 BootClassLoader,则使用 JVM 默认的库路径(java.library.path / Android 的 mLibPaths),拼接文件名,再调用 nativeLoad,同样,失败抛出异常。继续跟进。

到这里就是 native 函数了,就需要去看对应的 c 文件了,所以要重新去搜索了,这里的搜索方法就是 类名_函数名 的形式,转换过去就是 Runtime_nativeLoad 函数。
JNIEXPORT jstring JNICALL
Runtime_nativeLoad(JNIEnv* env, jclass ignored, jstring javaFilename,
jobject javaLoader, jclass caller)
{
return JVM_NativeLoad(env, javaFilename, javaLoader, caller);
}
这里就是正常的返回,直接走 JVM_NativeLoad(env, javaFilename, javaLoader, caller); 。继续跟进。
JNIEXPORT jstring JVM_NativeLoad(JNIEnv* env,
jstring javaFilename,
jobject javaLoader,
jclass caller) {
ScopedUtfChars filename(env, javaFilename);
if (filename.c_str() == nullptr) {
return nullptr;
}
std::string error_msg;
{
art::JavaVMExt* vm = art::Runtime::Current()->GetJavaVM();
bool success = vm->LoadNativeLibrary(env,
filename.c_str(),
javaLoader,
caller,
&error_msg);
if (success) {
return nullptr;
}
}
// Don't let a pending exception from JNI_OnLoad cause a CheckJNI issue with NewStringUTF.
env->ExceptionClear();
return env->NewStringUTF(error_msg.c_str());
}
该方法 首先将传进来的 so 库库名转为 C++ 字符串,然后获取当前 ART 运行时实例,并获取对应的 JavaVMExt 对象,再将多个函数传入到 LoadNativeLibrary 函数中,如果成功,返回 true,失败则返回 false 并 填充 error_msg。后面是异常处理部分,就没什么好说的了,继续跟进。
bool JavaVMExt::LoadNativeLibrary(JNIEnv* env,
const std::string& path,
jobject class_loader,
jclass caller_class,
std::string* error_msg) {
error_msg->clear();
// See if we've already loaded this library. If we have, and the class loader
// matches, return successfully without doing anything.
// TODO: for better results we should canonicalize the pathname (or even compare
// inodes). This implementation is fine if everybody is using System.loadLibrary.
SharedLibrary* library;
Thread* self = Thread::Current();
{
// TODO: move the locking (and more of this logic) into Libraries.
MutexLock mu(self, *Locks::jni_libraries_lock_);
library = libraries_->Get(path);
}
void* class_loader_allocator = nullptr;
std::string caller_location;
{
ScopedObjectAccess soa(env);
// As the incoming class loader is reachable/alive during the call of this function,
// it's okay to decode it without worrying about unexpectedly marking it alive.
ObjPtr<mirror::ClassLoader> loader = soa.Decode<mirror::ClassLoader>(class_loader);
ClassLinker* class_linker = Runtime::Current()->GetClassLinker();
if (class_linker->IsBootClassLoader(loader)) {
loader = nullptr;
class_loader = nullptr;
}
if (caller_class != nullptr) {
ObjPtr<mirror::Class> caller = soa.Decode<mirror::Class>(caller_class);
ObjPtr<mirror::DexCache> dex_cache = caller->GetDexCache();
if (dex_cache != nullptr) {
caller_location = dex_cache->GetLocation()->ToModifiedUtf8();
}
}
class_loader_allocator = class_linker->GetAllocatorForClassLoader(loader);
CHECK(class_loader_allocator != nullptr);
}
if (library != nullptr) {
// Use the allocator pointers for class loader equality to avoid unnecessary weak root decode.
if (library->GetClassLoaderAllocator() != class_loader_allocator) {
// The library will be associated with class_loader. The JNI
// spec says we can't load the same library into more than one
// class loader.
//
// This isn't very common. So spend some time to get a readable message.
auto call_to_string = [&](jobject obj) -> std::string {
if (obj == nullptr) {
return "null";
}
// Handle jweaks. Ignore double local-ref.
ScopedLocalRef<jobject> local_ref(env, env->NewLocalRef(obj));
if (local_ref != nullptr) {
ScopedLocalRef<jclass> local_class(env, env->GetObjectClass(local_ref.get()));
jmethodID to_string = env->GetMethodID(local_class.get(),
"toString",
"()Ljava/lang/String;");
DCHECK(to_string != nullptr);
ScopedLocalRef<jobject> local_string(env,
env->CallObjectMethod(local_ref.get(), to_string));
if (local_string != nullptr) {
ScopedUtfChars utf(env, reinterpret_cast<jstring>(local_string.get()));
if (utf.c_str() != nullptr) {
return utf.c_str();
}
}
if (env->ExceptionCheck()) {
// We can't do much better logging, really. So leave it with a Describe.
env->ExceptionDescribe();
env->ExceptionClear();
}
return "(Error calling toString)";
}
return "null";
};
std::string old_class_loader = call_to_string(library->GetClassLoader());
std::string new_class_loader = call_to_string(class_loader);
StringAppendF(error_msg, "Shared library \"%s\" already opened by "
"ClassLoader %p(%s); can't open in ClassLoader %p(%s)",
path.c_str(),
library->GetClassLoader(),
old_class_loader.c_str(),
class_loader,
new_class_loader.c_str());
LOG(WARNING) << *error_msg;
return false;
}
VLOG(jni) << "[Shared library \"" << path << "\" already loaded in "
<< " ClassLoader " << class_loader << "]";
if (!library->CheckOnLoadResult()) {
StringAppendF(error_msg, "JNI_OnLoad failed on a previous attempt "
"to load \"%s\"", path.c_str());
return false;
}
return true;
}
// Open the shared library. Because we're using a full path, the system
// doesn't have to search through LD_LIBRARY_PATH. (It may do so to
// resolve this library's dependencies though.)
// Failures here are expected when java.library.path has several entries
// and we have to hunt for the lib.
// Below we dlopen but there is no paired dlclose, this would be necessary if we supported
// class unloading. Libraries will only be unloaded when the reference count (incremented by
// dlopen) becomes zero from dlclose.
// Retrieve the library path from the classloader, if necessary.
ScopedLocalRef<jstring> library_path(env, GetLibrarySearchPath(env, class_loader));
Locks::mutator_lock_->AssertNotHeld(self);
const char* path_str = path.empty() ? nullptr : path.c_str();
bool needs_native_bridge = false;
char* nativeloader_error_msg = nullptr;
void* handle = android::OpenNativeLibrary(
env,
runtime_->GetTargetSdkVersion(),
path_str,
class_loader,
(caller_location.empty() ? nullptr : caller_location.c_str()),
library_path.get(),
&needs_native_bridge,
&nativeloader_error_msg);
VLOG(jni) << "[Call to dlopen(\"" << path << "\", RTLD_NOW) returned " << handle << "]";
if (handle == nullptr) {
*error_msg = nativeloader_error_msg;
android::NativeLoaderFreeErrorMessage(nativeloader_error_msg);
VLOG(jni) << "dlopen(\"" << path << "\", RTLD_NOW) failed: " << *error_msg;
return false;
}
if (env->ExceptionCheck() == JNI_TRUE) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Unexpected exception:";
env->ExceptionDescribe();
env->ExceptionClear();
}
// Create a new entry.
// TODO: move the locking (and more of this logic) into Libraries.
bool created_library = false;
{
// Create SharedLibrary ahead of taking the libraries lock to maintain lock ordering.
std::unique_ptr<SharedLibrary> new_library(
new SharedLibrary(env,
self,
path,
handle,
needs_native_bridge,
class_loader,
class_loader_allocator));
MutexLock mu(self, *Locks::jni_libraries_lock_);
library = libraries_->Get(path);
if (library == nullptr) { // We won race to get libraries_lock.
library = new_library.release();
libraries_->Put(path, library);
created_library = true;
}
}
if (!created_library) {
LOG(INFO) << "WOW: we lost a race to add shared library: "
<< "\"" << path << "\" ClassLoader=" << class_loader;
return library->CheckOnLoadResult();
}
VLOG(jni) << "[Added shared library \"" << path << "\" for ClassLoader " << class_loader << "]";
bool was_successful = false;
void* sym = library->FindSymbol("JNI_OnLoad", nullptr, android::kJNICallTypeRegular);
if (sym == nullptr) {
VLOG(jni) << "[No JNI_OnLoad found in \"" << path << "\"]";
was_successful = true;
} else {
// Call JNI_OnLoad. We have to override the current class
// loader, which will always be "null" since the stuff at the
// top of the stack is around Runtime.loadLibrary(). (See
// the comments in the JNI FindClass function.)
ScopedLocalRef<jobject> old_class_loader(env, env->NewLocalRef(self->GetClassLoaderOverride()));
self->SetClassLoaderOverride(class_loader);
VLOG(jni) << "[Calling JNI_OnLoad in \"" << path << "\"]";
using JNI_OnLoadFn = int(*)(JavaVM*, void*);
JNI_OnLoadFn jni_on_load = reinterpret_cast<JNI_OnLoadFn>(sym);
int version = (*jni_on_load)(this, nullptr);
if (IsSdkVersionSetAndAtMost(runtime_->GetTargetSdkVersion(), SdkVersion::kL)) {
// Make sure that sigchain owns SIGSEGV.
EnsureFrontOfChain(SIGSEGV);
}
self->SetClassLoaderOverride(old_class_loader.get());
if (version == JNI_ERR) {
StringAppendF(error_msg, "JNI_ERR returned from JNI_OnLoad in \"%s\"", path.c_str());
} else if (JavaVMExt::IsBadJniVersion(version)) {
StringAppendF(error_msg, "Bad JNI version returned from JNI_OnLoad in \"%s\": %d",
path.c_str(), version);
// It's unwise to call dlclose() here, but we can mark it
// as bad and ensure that future load attempts will fail.
// We don't know how far JNI_OnLoad got, so there could
// be some partially-initialized stuff accessible through
// newly-registered native method calls. We could try to
// unregister them, but that doesn't seem worthwhile.
} else {
was_successful = true;
}
VLOG(jni) << "[Returned " << (was_successful ? "successfully" : "failure")
<< " from JNI_OnLoad in \"" << path << "\"]";
}
library->SetResult(was_successful);
return was_successful;
}
首先,该方法先进行初始化和查找已加载库,ART 会维护一个 libraries_ 哈希表,记录已经成功加载的 native 库,通过该表来检查是否已经加载过(并加锁保护,防止多个线程同时加载同一库);ScopedObjectAccess 用于安全访问 Java 对象,Decode 把 jobject 转成 ART 内部对象指针,然后获取 ClassLinker,再检查传进来的调用者 ClassLoader 是不是引导类加载器,为什么要做特殊处理?因为系统类加载器不记录 native 库,直接置为 nullptr;接着获取调用类所在的 Dex 文件位置,用于日志或调试;然后获取 ClassLoader 分配器,因为 ART 每个 ClassLoader 都有一个 allocator(内存分配标识),用于区分库属于哪个 ClassLoader(注:JNI 规范要求:同一个 native 库不能加载到不同的 ClassLoader),获取到了之后就会进行检查是否 重复加载,如果不一致,说明已经被加载过了,报错,如果一致,再检查 JNI_OnLoad 是否成功。
解下来是核心逻辑,调用 OpenNativeLibrary ,内部会根据入参中的 class_loader 的 nativeLibraryPath(s)(通常是 /data/app/.../lib/arm/ 或 /system/lib/)去找 .so 文件,最终会调用到 dlopen 来加载动态库,返回 so 文件的 dlopen 句柄,如果加载失败,错误信息会写到 error_msg 中,这里没有 dlclose,注释里也解释清楚了,因为 ART/Java 默认不支持类卸载,所以即使 classloader 被 GC 回收,库也不会 dlclose,因此 so 文件一旦加载成功,就常驻进程,直到进程退出;后续的逻辑会为每个 so 文件生成一个 SharedLibrary 对象,保存 path、dlopen 句柄、class_loader、是否需要 native bridge(比如 32bit <-> 64bit 兼容),并放到 libraries_ 这个全局表里,保证重复加载时能复用;然后调用 JNI_OnLoad,从已加载的 so 库中寻找有没有 JNI_OnLoad 函数,有的话就直接调用,最后便是设置结果并返回。继续跟进 OpenNativeLibrary 函数。
void* OpenNativeLibrary(JNIEnv* env,
int32_t target_sdk_version,
const char* path,
jobject class_loader,
const char* caller_location,
jstring library_path_j,
bool* needs_native_bridge,
char** error_msg) {
#if defined(ART_TARGET_ANDROID)
if (class_loader == nullptr) {
// class_loader is null only for the boot class loader (see
// IsBootClassLoader call in JavaVMExt::LoadNativeLibrary), i.e. the caller
// is in the boot classpath.
*needs_native_bridge = false;
if (caller_location != nullptr) {
std::optional<NativeLoaderNamespace> ns = FindApexNamespace(caller_location);
if (ns.has_value()) {
const android_dlextinfo dlextinfo = {
.flags = ANDROID_DLEXT_USE_NAMESPACE,
.library_namespace = ns.value().ToRawAndroidNamespace(),
};
void* handle = android_dlopen_ext(path, RTLD_NOW, &dlextinfo);
char* dlerror_msg = handle == nullptr ? strdup(dlerror()) : nullptr;
ALOGD("Load %s using APEX ns %s for caller %s: %s",
path,
ns.value().name().c_str(),
caller_location,
dlerror_msg == nullptr ? "ok" : dlerror_msg);
if (dlerror_msg != nullptr) {
*error_msg = dlerror_msg;
}
return handle;
}
}
// Check if the library is in NATIVELOADER_DEFAULT_NAMESPACE_LIBS and should
// be loaded from the kNativeloaderExtraLibs namespace.
{
Result<void*> handle = TryLoadNativeloaderExtraLib(path);
if (!handle.ok()) {
*error_msg = strdup(handle.error().message().c_str());
return nullptr;
}
if (handle.value() != nullptr) {
return handle.value();
}
}
// Handle issue b/349878424.
static bool bypass_loading_for_b349878424 = ShouldBypassLoadingForB349878424();
if (bypass_loading_for_b349878424 &&
(strcmp("libsobridge.so", path) == 0 || strcmp("libwalkstack.so", path) == 0)) {
// Load a different library to pretend the loading was successful. This
// allows the device to boot.
ALOGD("Loading libbase.so instead of %s due to b/349878424", path);
path = "libbase.so";
}
// Fall back to the system namespace. This happens for preloaded JNI
// libraries in the zygote.
void* handle = OpenSystemLibrary(path, RTLD_NOW);
char* dlerror_msg = handle == nullptr ? strdup(dlerror()) : nullptr;
ALOGD("Load %s using system ns (caller=%s): %s",
path,
caller_location == nullptr ? "<unknown>" : caller_location,
dlerror_msg == nullptr ? "ok" : dlerror_msg);
if (dlerror_msg != nullptr) {
*error_msg = dlerror_msg;
}
return handle;
}
// If the caller is in any of the system image partitions and the library is
// in the same partition then load it without regards to public library
// restrictions. This is only done if the library is specified by an absolute
// path, so we don't affect the lookup process for libraries specified by name
// only.
if (caller_location != nullptr &&
// Apps in the partition may have their own native libraries which should
// be loaded with the app's classloader namespace, so only do this for
// libraries in the partition-wide lib(64) directories.
nativeloader::IsPartitionNativeLibPath(path) &&
// Don't do this if the system image is older than V, to avoid any compat
// issues with apps and shared libs in them.
android::modules::sdklevel::IsAtLeastV()) {
nativeloader::ApiDomain caller_api_domain = nativeloader::GetApiDomainFromPath(caller_location);
if (caller_api_domain != nativeloader::API_DOMAIN_DEFAULT) {
nativeloader::ApiDomain library_api_domain = nativeloader::GetApiDomainFromPath(path);
if (library_api_domain == caller_api_domain) {
bool is_bridged = false;
if (library_path_j != nullptr) {
ScopedUtfChars library_path_utf_chars(env, library_path_j);
if (library_path_utf_chars[0] != '\0') {
is_bridged = NativeBridgeIsPathSupported(library_path_utf_chars.c_str());
}
}
Result<NativeLoaderNamespace> ns = GetNamespaceForApiDomain(caller_api_domain, is_bridged);
if (!ns.ok()) {
ALOGD("Failed to find ns for caller %s in API domain %d to load %s (is_bridged=%b): %s",
caller_location,
caller_api_domain,
path,
is_bridged,
ns.error().message().c_str());
*error_msg = strdup(ns.error().message().c_str());
return nullptr;
}
*needs_native_bridge = ns.value().IsBridged();
Result<void*> handle = ns.value().Load(path);
ALOGD("Load %s using ns %s for caller %s in same partition (is_bridged=%b): %s",
path,
ns.value().name().c_str(),
caller_location,
is_bridged,
handle.ok() ? "ok" : handle.error().message().c_str());
if (!handle.ok()) {
*error_msg = strdup(handle.error().message().c_str());
return nullptr;
}
return handle.value();
}
}
}
NativeLoaderNamespace* ns;
const char* ns_descr;
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> guard(g_namespaces_mutex);
ns = g_namespaces->FindNamespaceByClassLoader(env, class_loader);
ns_descr = "class loader";
if (ns == nullptr) {
// This is the case where the classloader was not created by ApplicationLoaders
// In this case we create an isolated not-shared namespace for it.
const std::string empty_dex_path;
Result<NativeLoaderNamespace*> res =
CreateClassLoaderNamespaceLocked(env,
target_sdk_version,
class_loader,
nativeloader::API_DOMAIN_DEFAULT,
/*is_shared=*/false,
empty_dex_path,
library_path_j,
/*permitted_path_j=*/nullptr,
/*uses_library_list_j=*/nullptr);
if (!res.ok()) {
ALOGD("Failed to create isolated ns for %s (caller=%s)",
path,
caller_location == nullptr ? "<unknown>" : caller_location);
*error_msg = strdup(res.error().message().c_str());
return nullptr;
}
ns = res.value();
ns_descr = "isolated";
}
}
*needs_native_bridge = ns->IsBridged();
Result<void*> handle = ns->Load(path);
ALOGD("Load %s using %s ns %s (caller=%s): %s",
path,
ns_descr,
ns->name().c_str(),
caller_location == nullptr ? "<unknown>" : caller_location,
handle.ok() ? "ok" : handle.error().message().c_str());
if (!handle.ok()) {
*error_msg = strdup(handle.error().message().c_str());
return nullptr;
}
return handle.value();
#else // !ART_TARGET_ANDROID
UNUSED(env, target_sdk_version, class_loader, caller_location);
// Do some best effort to emulate library-path support. It will not
// work for dependencies.
//
// Note: null has a special meaning and must be preserved.
std::string library_path; // Empty string by default.
if (library_path_j != nullptr && path != nullptr && path[0] != '/') {
ScopedUtfChars library_path_utf_chars(env, library_path_j);
library_path = library_path_utf_chars.c_str();
}
std::vector<std::string> library_paths = base::Split(library_path, ":");
for (const std::string& lib_path : library_paths) {
*needs_native_bridge = false;
const char* path_arg;
std::string complete_path;
if (path == nullptr) {
// Preserve null.
path_arg = nullptr;
} else {
complete_path = lib_path;
if (!complete_path.empty()) {
complete_path.append("/");
}
complete_path.append(path);
path_arg = complete_path.c_str();
}
void* handle = dlopen(path_arg, RTLD_NOW);
if (handle != nullptr) {
return handle;
}
if (NativeBridgeIsSupported(path_arg)) {
*needs_native_bridge = true;
handle = NativeBridgeLoadLibrary(path_arg, RTLD_NOW);
if (handle != nullptr) {
return handle;
}
*error_msg = strdup(NativeBridgeGetError());
} else {
*error_msg = strdup(dlerror());
}
}
return nullptr;
#endif // !ART_TARGET_ANDROID
}
总的来说该函数的作用就是根据传入的 class_loader / caller_location / library_path_j 等上下文,选择合适的 native loader namespace,然后最终调用 dlopen(或 android_dlopen_ext / native-bridge)加载目标 .so,返回 dlopen 的句柄。而这里的 android_dlopen_ext 函数也就是经常进行 Hook 的位置了。跟进。

根据看雪的那篇文章中所提及的,在 Android 12 中会直接调用到 __loader_android_dlopen_ext 函数,而在其他版本会调转到 mock->mock_dlopen_ext (如上图,会模拟 dlopen 的行为,同时通过 flag 和宏定义走到不同的函数位置)。
这里我们固定在 Android 12 的位置去实现。代码如下
void* __loader_android_dlopen_ext(const char* filename,
int flags,
const android_dlextinfo* extinfo,
const void* caller_addr) {
return dlopen_ext(filename, flags, extinfo, caller_addr);
}
跟进 dlopen_ext 函数。
static void* dlopen_ext(const char* filename,
int flags,
const android_dlextinfo* extinfo,
const void* caller_addr) {
ScopedPthreadMutexLocker locker(&g_dl_mutex);
g_linker_logger.ResetState();
void* result = do_dlopen(filename, flags, extinfo, caller_addr);
if (result == nullptr) {
__bionic_format_dlerror("dlopen failed", linker_get_error_buffer());
return nullptr;
}
return result;
}
同样进入 do_dlopen(filename, flags, extinfo, caller_addr),在这个函数中附加了很多对于 do_dlopen 函数参数的检测和判断。
void* do_dlopen(const char* name, int flags,
const android_dlextinfo* extinfo,
const void* caller_addr) {
std::string trace_prefix = std::string("dlopen: ") + (name == nullptr ? "(nullptr)" : name);
ScopedTrace trace(trace_prefix.c_str());
ScopedTrace loading_trace((trace_prefix + " - loading and linking").c_str());
soinfo* const caller = find_containing_library(caller_addr);
android_namespace_t* ns = get_caller_namespace(caller);
LD_LOG(kLogDlopen,
"dlopen(name=\"%s\", flags=0x%x, extinfo=%s, caller=\"%s\", caller_ns=%s@%p, targetSdkVersion=%i) ...",
name,
flags,
android_dlextinfo_to_string(extinfo).c_str(),
caller == nullptr ? "(null)" : caller->get_realpath(),
ns == nullptr ? "(null)" : ns->get_name(),
ns,
get_application_target_sdk_version());
auto purge_guard = android::base::make_scope_guard([&]() { purge_unused_memory(); });
auto failure_guard = android::base::make_scope_guard(
[&]() { LD_LOG(kLogDlopen, "... dlopen failed: %s", linker_get_error_buffer()); });
if ((flags & ~(RTLD_NOW|RTLD_LAZY|RTLD_LOCAL|RTLD_GLOBAL|RTLD_NODELETE|RTLD_NOLOAD)) != 0) {
DL_OPEN_ERR("invalid flags to dlopen: %x", flags);
return nullptr;
}
if (extinfo != nullptr) {
if ((extinfo->flags & ~(ANDROID_DLEXT_VALID_FLAG_BITS)) != 0) {
DL_OPEN_ERR("invalid extended flags to android_dlopen_ext: 0x%" PRIx64, extinfo->flags);
return nullptr;
}
if ((extinfo->flags & ANDROID_DLEXT_USE_LIBRARY_FD) == 0 &&
(extinfo->flags & ANDROID_DLEXT_USE_LIBRARY_FD_OFFSET) != 0) {
DL_OPEN_ERR("invalid extended flag combination (ANDROID_DLEXT_USE_LIBRARY_FD_OFFSET without "
"ANDROID_DLEXT_USE_LIBRARY_FD): 0x%" PRIx64, extinfo->flags);
return nullptr;
}
if ((extinfo->flags & ANDROID_DLEXT_USE_NAMESPACE) != 0) {
if (extinfo->library_namespace == nullptr) {
DL_OPEN_ERR("ANDROID_DLEXT_USE_NAMESPACE is set but extinfo->library_namespace is null");
return nullptr;
}
ns = extinfo->library_namespace;
}
}
// Workaround for dlopen(/system/lib/<soname>) when .so is in /apex. http://b/121248172
// The workaround works only when targetSdkVersion < Q.
std::string name_to_apex;
if (translateSystemPathToApexPath(name, &name_to_apex)) {
const char* new_name = name_to_apex.c_str();
LD_LOG(kLogDlopen, "dlopen considering translation from %s to APEX path %s",
name,
new_name);
// Some APEXs could be optionally disabled. Only translate the path
// when the old file is absent and the new file exists.
// TODO(b/124218500): Re-enable it once app compat issue is resolved
/*
if (file_exists(name)) {
LD_LOG(kLogDlopen, "dlopen %s exists, not translating", name);
} else
*/
if (!file_exists(new_name)) {
LD_LOG(kLogDlopen, "dlopen %s does not exist, not translating",
new_name);
} else {
LD_LOG(kLogDlopen, "dlopen translation accepted: using %s", new_name);
name = new_name;
}
}
// End Workaround for dlopen(/system/lib/<soname>) when .so is in /apex.
std::string translated_name_holder;
assert(!g_is_hwasan || !g_is_asan);
const char* translated_name = name;
if (g_is_asan && translated_name != nullptr && translated_name[0] == '/') {
char original_path[PATH_MAX];
if (realpath(name, original_path) != nullptr) {
translated_name_holder = std::string(kAsanLibDirPrefix) + original_path;
if (file_exists(translated_name_holder.c_str())) {
soinfo* si = nullptr;
if (find_loaded_library_by_realpath(ns, original_path, true, &si)) {
DL_WARN("linker_asan dlopen NOT translating \"%s\" -> \"%s\": library already loaded", name,
translated_name_holder.c_str());
} else {
DL_WARN("linker_asan dlopen translating \"%s\" -> \"%s\"", name, translated_name);
translated_name = translated_name_holder.c_str();
}
}
}
} else if (g_is_hwasan && translated_name != nullptr && translated_name[0] == '/') {
char original_path[PATH_MAX];
if (realpath(name, original_path) != nullptr) {
// Keep this the same as CreateHwasanPath in system/linkerconfig/modules/namespace.cc.
std::string path(original_path);
auto slash = path.rfind('/');
if (slash != std::string::npos || slash != path.size() - 1) {
translated_name_holder = path.substr(0, slash) + "/hwasan" + path.substr(slash);
}
if (!translated_name_holder.empty() && file_exists(translated_name_holder.c_str())) {
soinfo* si = nullptr;
if (find_loaded_library_by_realpath(ns, original_path, true, &si)) {
DL_WARN("linker_hwasan dlopen NOT translating \"%s\" -> \"%s\": library already loaded",
name, translated_name_holder.c_str());
} else {
DL_WARN("linker_hwasan dlopen translating \"%s\" -> \"%s\"", name, translated_name);
translated_name = translated_name_holder.c_str();
}
}
}
}
ProtectedDataGuard guard;
soinfo* si = find_library(ns, translated_name, flags, extinfo, caller);
loading_trace.End();
if (si != nullptr) {
void* handle = si->to_handle();
LD_LOG(kLogDlopen,
"... dlopen calling constructors: realpath=\"%s\", soname=\"%s\", handle=%p",
si->get_realpath(), si->get_soname(), handle);
si->call_constructors();
failure_guard.Disable();
LD_LOG(kLogDlopen,
"... dlopen successful: realpath=\"%s\", soname=\"%s\", handle=%p",
si->get_realpath(), si->get_soname(), handle);
return handle;
}
return nullptr;
}
int do_dladdr(const void* addr, Dl_info* info) {
// Determine if this address can be found in any library currently mapped.
soinfo* si = find_containing_library(addr);
if (si == nullptr) {
return 0;
}
memset(info, 0, sizeof(Dl_info));
info->dli_fname = si->get_realpath();
// Address at which the shared object is loaded.
info->dli_fbase = reinterpret_cast<void*>(si->base);
// Determine if any symbol in the library contains the specified address.
ElfW(Sym)* sym = si->find_symbol_by_address(addr);
if (sym != nullptr) {
info->dli_sname = si->get_string(sym->st_name);
info->dli_saddr = reinterpret_cast<void*>(si->resolve_symbol_address(sym));
}
return 1;
}
static soinfo* soinfo_from_handle(void* handle) {
if ((reinterpret_cast<uintptr_t>(handle) & 1) != 0) {
auto it = g_soinfo_handles_map.find(reinterpret_cast<uintptr_t>(handle));
if (it == g_soinfo_handles_map.end()) {
return nullptr;
} else {
return it->second;
}
}
return static_cast<soinfo*>(handle);
}
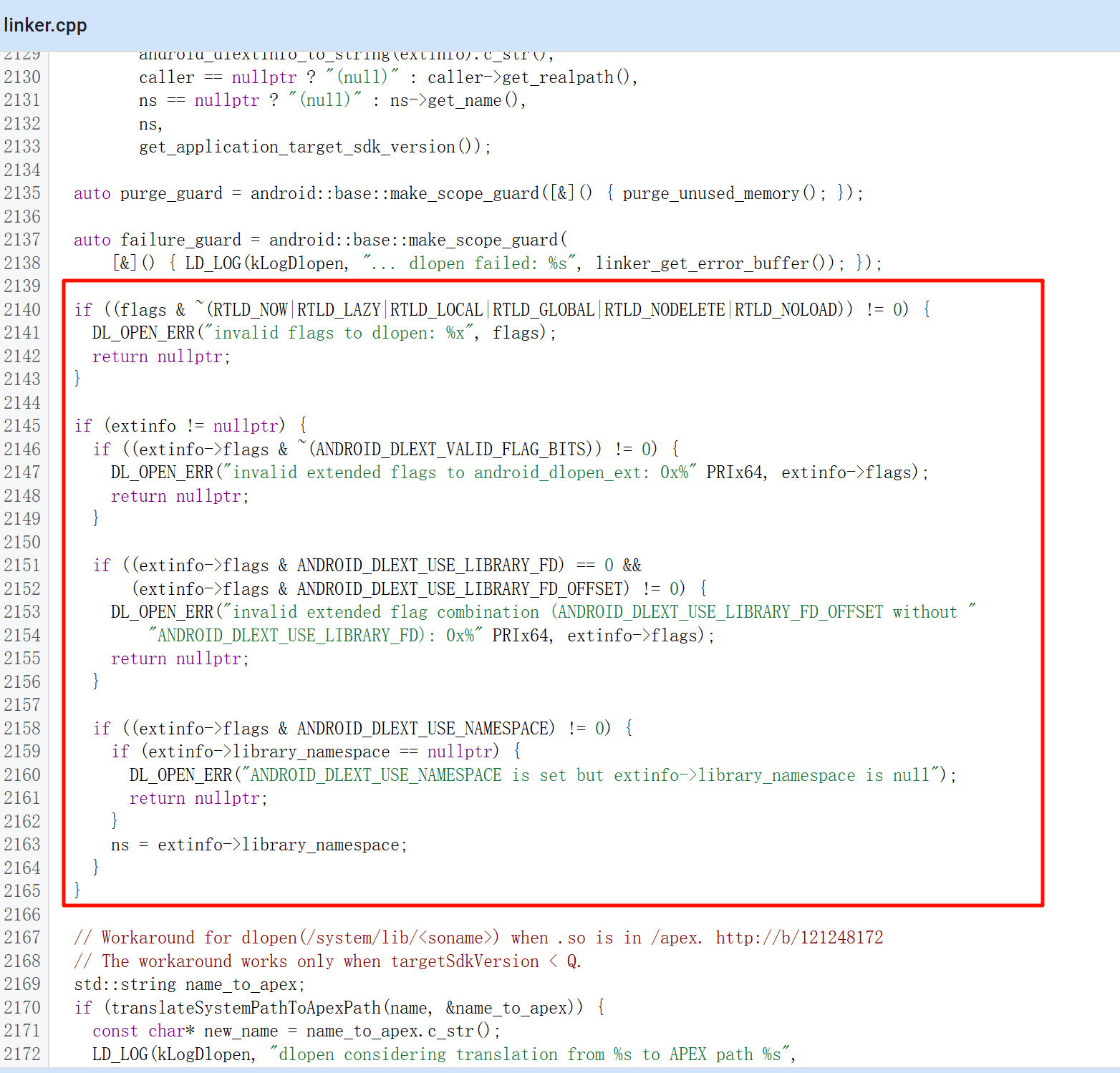
首先对 flags 进行校验,然后大面积的对传入的 extinfo 进行检查,接着对 APEX 路径进行翻译;调用 find_library 查找并加载库,即在 namespace 下查找库是否已加载,如果未加载,则解析 ELF、执行 mmap、解析依赖,返回 soinfo*(库的内部结构,包括基址、soname、symbols);然后调用构造函数,也就是对库的 .init_array 执行初始化函数(包括 JNI_OnLoad 会在上层封装调用),很多检测逻辑就会在写在这个段,在 JNI_OnLoad 函数之前运行。继续跟进 find_library(ns, translated_name, flags, extinfo, caller)。
static soinfo* find_library(android_namespace_t* ns,
const char* name, int rtld_flags,
const android_dlextinfo* extinfo,
soinfo* needed_by) {
soinfo* si = nullptr;
if (name == nullptr) {
si = solist_get_somain();
} else if (!find_libraries(ns,
needed_by,
&name,
1,
&si,
nullptr,
0,
rtld_flags,
extinfo,
false /* add_as_children */)) {
if (si != nullptr) {
soinfo_unload(si);
}
return nullptr;
}
si->increment_ref_count();
return si;
}
直接继续跟进 find_libraries 函数
bool find_libraries(android_namespace_t* ns,
soinfo* start_with,
const char* const library_names[],
size_t library_names_count,
soinfo* soinfos[],
std::vector<soinfo*>* ld_preloads,
size_t ld_preloads_count,
int rtld_flags,
const android_dlextinfo* extinfo,
bool add_as_children,
std::vector<android_namespace_t*>* namespaces) {
// Step 0: prepare.
std::unordered_map<const soinfo*, ElfReader> readers_map;
LoadTaskList load_tasks;
for (size_t i = 0; i < library_names_count; ++i) {
const char* name = library_names[i];
load_tasks.push_back(LoadTask::create(name, start_with, ns, &readers_map));
}
// If soinfos array is null allocate one on stack.
// The array is needed in case of failure; for example
// when library_names[] = {libone.so, libtwo.so} and libone.so
// is loaded correctly but libtwo.so failed for some reason.
// In this case libone.so should be unloaded on return.
// See also implementation of failure_guard below.
if (soinfos == nullptr) {
size_t soinfos_size = sizeof(soinfo*)*library_names_count;
soinfos = reinterpret_cast<soinfo**>(alloca(soinfos_size));
memset(soinfos, 0, soinfos_size);
}
// list of libraries to link - see step 2.
size_t soinfos_count = 0;
auto scope_guard = android::base::make_scope_guard([&]() {
for (LoadTask* t : load_tasks) {
LoadTask::deleter(t);
}
});
ZipArchiveCache zip_archive_cache;
soinfo_list_t new_global_group_members;
// Step 1: expand the list of load_tasks to include
// all DT_NEEDED libraries (do not load them just yet)
for (size_t i = 0; i<load_tasks.size(); ++i) {
LoadTask* task = load_tasks[i];
soinfo* needed_by = task->get_needed_by();
bool is_dt_needed = needed_by != nullptr && (needed_by != start_with || add_as_children);
task->set_extinfo(is_dt_needed ? nullptr : extinfo);
task->set_dt_needed(is_dt_needed);
// Note: start from the namespace that is stored in the LoadTask. This namespace
// is different from the current namespace when the LoadTask is for a transitive
// dependency and the lib that created the LoadTask is not found in the
// current namespace but in one of the linked namespaces.
android_namespace_t* start_ns = const_cast<android_namespace_t*>(task->get_start_from());
LD_LOG(kLogDlopen, "find_library_internal(ns=%s@%p): task=%s, is_dt_needed=%d",
start_ns->get_name(), start_ns, task->get_name(), is_dt_needed);
if (!find_library_internal(start_ns, task, &zip_archive_cache, &load_tasks, rtld_flags)) {
return false;
}
soinfo* si = task->get_soinfo();
if (is_dt_needed) {
needed_by->add_child(si);
}
// When ld_preloads is not null, the first
// ld_preloads_count libs are in fact ld_preloads.
bool is_ld_preload = false;
if (ld_preloads != nullptr && soinfos_count < ld_preloads_count) {
ld_preloads->push_back(si);
is_ld_preload = true;
}
if (soinfos_count < library_names_count) {
soinfos[soinfos_count++] = si;
}
// Add the new global group members to all initial namespaces. Do this secondary namespace setup
// at the same time that libraries are added to their primary namespace so that the order of
// global group members is the same in the every namespace. Only add a library to a namespace
// once, even if it appears multiple times in the dependency graph.
if (is_ld_preload || (si->get_dt_flags_1() & DF_1_GLOBAL) != 0) {
if (!si->is_linked() && namespaces != nullptr && !new_global_group_members.contains(si)) {
new_global_group_members.push_back(si);
for (auto linked_ns : *namespaces) {
if (si->get_primary_namespace() != linked_ns) {
linked_ns->add_soinfo(si);
si->add_secondary_namespace(linked_ns);
}
}
}
}
}
// Step 2: Load libraries in random order (see b/24047022)
LoadTaskList load_list;
for (auto&& task : load_tasks) {
soinfo* si = task->get_soinfo();
auto pred = [&](const LoadTask* t) {
return t->get_soinfo() == si;
};
if (!si->is_linked() &&
std::find_if(load_list.begin(), load_list.end(), pred) == load_list.end() ) {
load_list.push_back(task);
}
}
bool reserved_address_recursive = false;
if (extinfo) {
reserved_address_recursive = extinfo->flags & ANDROID_DLEXT_RESERVED_ADDRESS_RECURSIVE;
}
if (!reserved_address_recursive) {
// Shuffle the load order in the normal case, but not if we are loading all
// the libraries to a reserved address range.
shuffle(&load_list);
}
// Set up address space parameters.
address_space_params extinfo_params, default_params;
size_t relro_fd_offset = 0;
if (extinfo) {
if (extinfo->flags & ANDROID_DLEXT_RESERVED_ADDRESS) {
extinfo_params.start_addr = extinfo->reserved_addr;
extinfo_params.reserved_size = extinfo->reserved_size;
extinfo_params.must_use_address = true;
} else if (extinfo->flags & ANDROID_DLEXT_RESERVED_ADDRESS_HINT) {
extinfo_params.start_addr = extinfo->reserved_addr;
extinfo_params.reserved_size = extinfo->reserved_size;
}
}
for (auto&& task : load_list) {
address_space_params* address_space =
(reserved_address_recursive || !task->is_dt_needed()) ? &extinfo_params : &default_params;
if (!task->load(address_space)) {
return false;
}
}
// The WebView loader uses RELRO sharing in order to promote page sharing of the large RELRO
// segment, as it's full of C++ vtables. Because MTE globals, by default, applies random tags to
// each global variable, the RELRO segment is polluted and unique for each process. In order to
// allow sharing, but still provide some protection, we use deterministic global tagging schemes
// for DSOs that are loaded through android_dlopen_ext, such as those loaded by WebView.
bool dlext_use_relro =
extinfo && extinfo->flags & (ANDROID_DLEXT_WRITE_RELRO | ANDROID_DLEXT_USE_RELRO);
// Step 3: pre-link all DT_NEEDED libraries in breadth first order.
bool any_memtag_stack = false;
for (auto&& task : load_tasks) {
soinfo* si = task->get_soinfo();
if (!si->is_linked() && !si->prelink_image(dlext_use_relro)) {
return false;
}
// si->memtag_stack() needs to be called after si->prelink_image() which populates
// the dynamic section.
if (si->memtag_stack()) {
any_memtag_stack = true;
LD_LOG(kLogDlopen,
"... load_library requesting stack MTE for: realpath=\"%s\", soname=\"%s\"",
si->get_realpath(), si->get_soname());
}
register_soinfo_tls(si);
}
if (any_memtag_stack) {
if (auto* cb = __libc_shared_globals()->memtag_stack_dlopen_callback) {
cb();
} else {
// find_library is used by the initial linking step, so we communicate that we
// want memtag_stack enabled to __libc_init_mte.
__libc_shared_globals()->initial_memtag_stack_abi = true;
}
}
// Step 4: Construct the global group. DF_1_GLOBAL bit is force set for LD_PRELOADed libs because
// they must be added to the global group. Note: The DF_1_GLOBAL bit for a library is normally set
// in step 3.
if (ld_preloads != nullptr) {
for (auto&& si : *ld_preloads) {
si->set_dt_flags_1(si->get_dt_flags_1() | DF_1_GLOBAL);
}
}
// Step 5: Collect roots of local_groups.
// Whenever needed_by->si link crosses a namespace boundary it forms its own local_group.
// Here we collect new roots to link them separately later on. Note that we need to avoid
// collecting duplicates. Also the order is important. They need to be linked in the same
// BFS order we link individual libraries.
std::vector<soinfo*> local_group_roots;
if (start_with != nullptr && add_as_children) {
local_group_roots.push_back(start_with);
} else {
CHECK(soinfos_count == 1);
local_group_roots.push_back(soinfos[0]);
}
for (auto&& task : load_tasks) {
soinfo* si = task->get_soinfo();
soinfo* needed_by = task->get_needed_by();
bool is_dt_needed = needed_by != nullptr && (needed_by != start_with || add_as_children);
android_namespace_t* needed_by_ns =
is_dt_needed ? needed_by->get_primary_namespace() : ns;
if (!si->is_linked() && si->get_primary_namespace() != needed_by_ns) {
auto it = std::find(local_group_roots.begin(), local_group_roots.end(), si);
LD_LOG(kLogDlopen,
"Crossing namespace boundary (si=%s@%p, si_ns=%s@%p, needed_by=%s@%p, ns=%s@%p, needed_by_ns=%s@%p) adding to local_group_roots: %s",
si->get_realpath(),
si,
si->get_primary_namespace()->get_name(),
si->get_primary_namespace(),
needed_by == nullptr ? "(nullptr)" : needed_by->get_realpath(),
needed_by,
ns->get_name(),
ns,
needed_by_ns->get_name(),
needed_by_ns,
it == local_group_roots.end() ? "yes" : "no");
if (it == local_group_roots.end()) {
local_group_roots.push_back(si);
}
}
}
// Step 6: Link all local groups
for (auto root : local_group_roots) {
soinfo_list_t local_group;
android_namespace_t* local_group_ns = root->get_primary_namespace();
walk_dependencies_tree(root,
[&] (soinfo* si) {
if (local_group_ns->is_accessible(si)) {
local_group.push_back(si);
return kWalkContinue;
} else {
return kWalkSkip;
}
});
soinfo_list_t global_group = local_group_ns->get_global_group();
SymbolLookupList lookup_list(global_group, local_group);
soinfo* local_group_root = local_group.front();
bool linked = local_group.visit([&](soinfo* si) {
// Even though local group may contain accessible soinfos from other namespaces
// we should avoid linking them (because if they are not linked -> they
// are in the local_group_roots and will be linked later).
if (!si->is_linked() && si->get_primary_namespace() == local_group_ns) {
const android_dlextinfo* link_extinfo = nullptr;
if (si == soinfos[0] || reserved_address_recursive) {
// Only forward extinfo for the first library unless the recursive
// flag is set.
link_extinfo = extinfo;
}
if (__libc_shared_globals()->load_hook) {
__libc_shared_globals()->load_hook(si->load_bias, si->phdr, si->phnum);
}
lookup_list.set_dt_symbolic_lib(si->has_DT_SYMBOLIC ? si : nullptr);
if (!si->link_image(lookup_list, local_group_root, link_extinfo, &relro_fd_offset) ||
!get_cfi_shadow()->AfterLoad(si, solist_get_head())) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
});
if (!linked) {
return false;
}
}
// Step 7: Mark all load_tasks as linked and increment refcounts
// for references between load_groups (at this point it does not matter if
// referenced load_groups were loaded by previous dlopen or as part of this
// one on step 6)
if (start_with != nullptr && add_as_children) {
start_with->set_linked();
}
for (auto&& task : load_tasks) {
soinfo* si = task->get_soinfo();
si->set_linked();
}
for (auto&& task : load_tasks) {
soinfo* si = task->get_soinfo();
soinfo* needed_by = task->get_needed_by();
if (needed_by != nullptr &&
needed_by != start_with &&
needed_by->get_local_group_root() != si->get_local_group_root()) {
si->increment_ref_count();
}
}
return true;
}
static soinfo* find_library(android_namespace_t* ns,
const char* name, int rtld_flags,
const android_dlextinfo* extinfo,
soinfo* needed_by) {
soinfo* si = nullptr;
if (name == nullptr) {
si = solist_get_somain();
} else if (!find_libraries(ns,
needed_by,
&name,
1,
&si,
nullptr,
0,
rtld_flags,
extinfo,
false /* add_as_children */)) {
if (si != nullptr) {
soinfo_unload(si);
}
return nullptr;
}
si->increment_ref_count();
return si;
}
这部分代码很长,在安卓源码中也有对齐进行了批注,一步一步地去加载和解析 so 文件,去实现 so 文件的加载。
Step 0:准备 load_tasks 和 soinfos
- 每个库对应一个 LoadTask,保存库名、namespace、依赖信息;
- 如果 soinfos 为 null,临时在栈上分配并构造,用于回滚失败(即如果某个库加载失败,要卸载前面已经加载的库)。
for (size_t i = 0; i < library_names_count; ++i) {
load_tasks.push_back(LoadTask::create(name, start_with, ns, &readers_map));
}
Step 1:扩展 DT_NEEDED 依赖
- 对每个 LoadTask,查找它的依赖库(DT_NEEDED);
- 注意:先不真正加载 DT_NEEDED 的库,只是把它们加入 load_tasks 队列;
- is_dt_need 表示当前库是依赖库还是主库,主库可以使用 extinfo(比如保留地址);
- 如果 find_library_internal 失败,直接返回 false;
- LD_PRELOAD 的库必须加入全局组(DF_1_GLOBAL);
- 可选地把库添加到其他 namespace,实现跨 namespace 可见。
for (size_t i = 0; i<load_tasks.size(); ++i) {
LoadTask* task = load_tasks[i];
bool is_dt_needed = needed_by != nullptr && (needed_by != start_with || add_as_children);
task->set_extinfo(is_dt_needed ? nullptr : extinfo);
task->set_dt_needed(is_dt_needed);
if (!find_library_internal(start_ns, task, &zip_archive_cache, &load_tasks, rtld_flags)) {
return false;
}
}
if (ld_preloads != nullptr && soinfos_count < ld_preloads_count) {
ld_preloads->push_back(si);
}
if (is_ld_preload || (si->get_dt_flags_1() & DF_1_GLOBAL) != 0) {
for (auto linked_ns : *namespaces) {
linked_ns->add_soinfo(si);
si->add_secondary_namespace(linked_ns);
}
}
Step 2:加载库的顺序处理
- 将待加载库整理到 load_list;
- 随机顺序加载:为了避免库依赖顺序错误;
- 如果使用保留地址(ANDROID_DLEXT_RESERVED_ADDRESS_RECURSIVE),则不打乱顺序。
LoadTaskList load_list;
for (auto&& task : load_tasks) { ... }
shuffle(&load_list);
Step 3:预链接 DT_NEEDED 库
- 预解析动态节(.dynamic),计算符号表、依赖关系;
- 支持 RELRO(只读重定位段)共享,提升 WebView 等库安全性;
- 对 ELF 文件结构进行检查,只有对应的 so 文件时完整的才能进行加载链接;
- 将 soinfo 注册到 TLS 段。
bool any_memtag_stack = false;
for (auto&& task : load_tasks) {
soinfo* si = task->get_soinfo();
if (!si->is_linked() && !si->prelink_image(dlext_use_relro)) {
return false;
}
// si->memtag_stack() needs to be called after si->prelink_image() which populates
// the dynamic section.
if (si->memtag_stack()) {
any_memtag_stack = true;
LD_LOG(kLogDlopen,
"... load_library requesting stack MTE for: realpath=\"%s\", soname=\"%s\"",
si->get_realpath(), si->get_soname());
}
register_soinfo_tls(si);
}
Step 4:处理全局符号解析
- 设置 LD_PRELOAD 库为全局,该库必须全局可见,以便后续库解析符号。
if (ld_preloads != nullptr) {
for (auto&& si : *ld_preloads) {
si->set_dt_flags_1(si->get_dt_flags_1() | DF_1_GLOBAL);
}
}
Step 5 — 7:这几步就很细节了,确定哪些库是 local_group 的根节点,用于处理跨 namespace 的依赖,保证跨 namespace 的库在独立的 local_group 内被链接,不干扰其他 namespace;遍历每个 local_group root 的依赖树,对每个库 调用 link_image,执行 ELF load / mmap、Relocation、符号解析、RELRO / memtag 支持,即保证依赖库按正确顺序链接,支持 namespace 隔离和安全特性;管理生命周期,保证库在依赖的期间不会被卸载。
至此,整个 so 文件被全部解析处理。
三、总结
重新梳理一下整个 so 文件加载过程,我们首先通过 System.load() 进入,此方法最终调用 Runtime.loadLibrary0(),然后进入 nativeLoad() 函数,nativeLoad –> JVM_NativeLoad,接着进入 JavaVMExt::LoadNativeLibrary 方法后,最终会调用 dlopen 进行真正的 so 文件加载(在 Android 12 及以上版本,会调用 android_dlopen_ext 返回 __loader_android_dlopen_ext),该方法最终调用 dlopen_ext();再就是 do_dlopen(),在该函数中,会调用 find_library() 进行 SO 文件的真正加载。
这里是对于soinfo的赋值,同时在这里开始调用so的.init_proc函数,接着调用.init_array中的函数,最后才是JNI_OnLoad函数。最后到达find_libraries 执行最后的处理。
附上文章中的流程图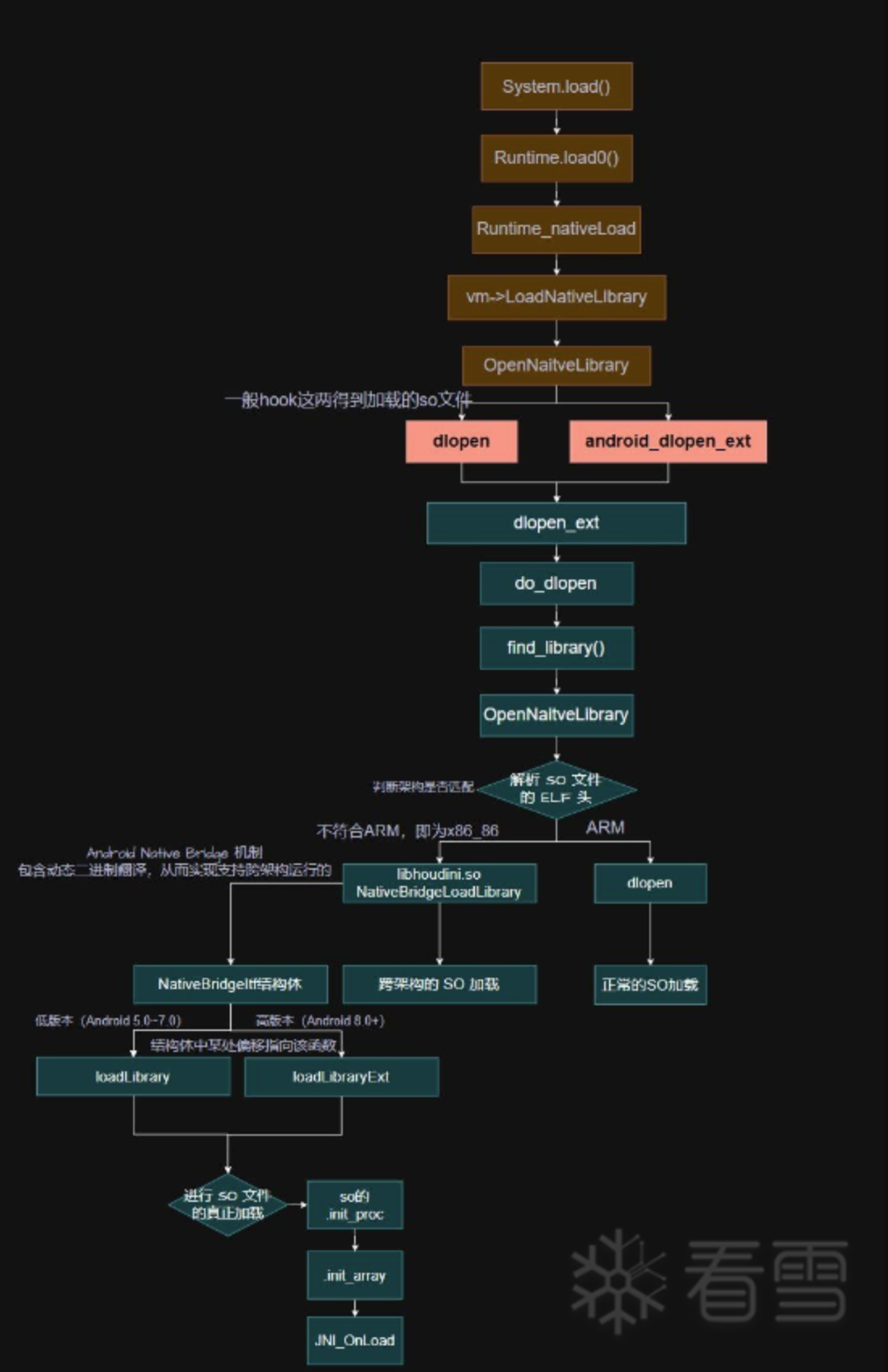
转载请注明来源,欢迎对文章中的引用来源进行考证,欢迎指出任何有错误或不够清晰的表达。可以在下面评论区评论,也可以邮件至 1621925986@qq.com

