Dex 文件结构学习
一、前言
为了更好的学习 Android 加固,所以还是打算好好学一下 Dex 文件结构,于是在 看雪 上找到了一篇蛮详细的文章进行学习。
二、开始
准备阶段
自行编译 dex 文件供后续分析
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.printf("Hello and welcome!\n");
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
System.out.println("i = " + i);
}
}
}
编译指令
javac Main.java
d8 --output=dex_out/ Main.class
即可得到一个 dex 文件。
数据类型
Android 源码 http://androidxref.com/2.3.7/xref/dalvik/libdex/DexFile.h (但是现在访问不了了),定义了 dex 文件用到的数据结构
| 自定义类型 | 原类型 | 含义 |
|---|---|---|
| s1 | int8_t | 有符号单字节 |
| u1 | uint8_t | 无符号单字节 |
| s2 | int16_t | |
| u2 | uint16_t | |
| s4 | int32_t | |
| u4 | uint32_t | |
| s8 | int64_t | |
| u8 | uint64_t | |
| sleb128 | 无 | 有符号LEB128,可变长度 |
| uleb128 | 无 | 无符号LEB128,可变长度 |
| uleb128p1 | 无 | 等于ULEB128加1,可变长度 |
Leb 128
sleb 128、uleb 128、uleb 128p1 是 dex 文件中特有的 LEB 128 类型,在下述 Android 源码位置可以找到 LEB 128 的实现。http://androidxref.com/2.3.7/xref/dalvik/libdex/Leb128.h。
每个 LEB 128 由 1- 5 字节组成,所有字节组合在一起标识一个 32 位 的数据,每个字节只有低 7 位为有效位,最高位需要用来标识是否需要使用额外字节。
如果第一个字节的最高位为 1,表示 LEB 128 需要使用第二个字节,如果第二个字节的最高位为 1,表示会使用第三个字节,依次类推,直到最后一个字节的最高位为 0。
- 下面举个例子
- 300(10) = 100101100(2)。然后按 7 位一组,从低位开始切分
- 100101100
= [0010110] [0010]- 组装字节
- 第一个字节,由于后面还有字节->最高位设为 1,得到,10101100 = 0xAC
- 第二个字节,没有后续 -> 故最高位设为 0,得到,00000010 = 0x02
- 最终编码
300 -> [0xAC, 0x02]
uleb 128 读取代码如下。值得注意的是参数为二级指针,也就是说,调用该函数时移动一级指针,一级指针的偏移量所指即为读取到的 uleb 128 的大小。
int readUnsignedLeb128(const u1** pStream) {
const u1* ptr = *pStream;
int result = *(ptr++);
if (result > 0x7f) {
int cur = *(ptr++);
result = (result & 0x7f) | ((cur & 0x7f) << 7);
if (cur > 0x7f) {
cur = *(ptr++);
result |= (cur & 0x7f) << 14;
if (cur > 0x7f) {
cur = *(ptr++);
result |= (cur & 0x7f) << 21;
if (cur > 0x7f) {
/*
* Note: We don't check to see if cur is out of
* range here, meaning we tolerate garbage in the
* high four-order bits.
*/
cur = *(ptr++);
result |= cur << 28;
}
}
}
}
*pStream = ptr;
return result;
}
为方便使用自定义的 myReadUnsignedLeb128 函数,参数为一级指针,返回读取的数据及其大小。
// 传入指针直接读取数据并返回数据和读取的大小(可选)
int myReadUnsignedLeb128(const u1* pData,size_t* readSize) {
const u1** pStream = &pData;
u4 result=readUnsignedLeb128(pStream);
if(readSize)
*readSize=unsignedLeb128Size(result);
return result;
}
encoded_value
参考 Android 官方文档 https://source.android.com/docs/core/dalvik/dex-format?hl=zh-cn#encoding 。
解析 DexClassDef 结构 时,Annotation 的 annotation_element 和 encoded_array_item 会使用该编码。
编码格式如下,1 字节的头用于指定 value 格式和大小,后续紧跟数据,需要根据类型解析。
| 名称 | 格式 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| (value_arg << 5) | value_type | ubyte | 高3位为value_arg的值,低5位为value_type的值,value_type指定value的格式。 |
| value | ubyte[] | 用于表示值的字节,不同 value_type 字节的长度不同且采用不同的解译方式;不过一律采用小端字节序。 |
value_type 枚举定义如下:
| 类型名称 | value_type | value_arg | value格式 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VALUE_BYTE | 0x00 | (无;必须为 0) |
ubyte[1] | 有符号的单字节整数值 |
| VALUE_SHORT | 0x02 | size - 1 (0…1) | ubyte[size] | 有符号的双字节整数值,符号扩展 |
| VALUE_CHAR | 0x03 | size - 1 (0…1) | ubyte[size] | 无符号的双字节整数值,零扩展 |
| VALUE_INT | 0x04 | size - 1 (0…3) | ubyte[size] | 有符号的四字节整数值,符号扩展 |
| VALUE_LONG | 0x06 | size - 1 (0…7) | ubyte[size] | 有符号的八字节整数值,符号扩展 |
| VALUE_FLOAT | 0x10 | size - 1 (0…3) | ubyte[size] | 四字节位模式,向右零扩展,系统会将其解译为 IEEE754 32 位浮点值 |
| VALUE_DOUBLE | 0x11 | size - 1 (0…7) | ubyte[size] | 八字节位模式,向右零扩展,系统会将其解译为 IEEE754 64 位浮点值 |
| VALUE_METHOD_TYPE | 0x15 | size - 1 (0…3) | ubyte[size] | 无符号(零扩展)四字节整数值,会被解译为要编入 proto_ids 区段的索引;表示方法类型值 |
| VALUE_METHOD_HANDLE | 0x16 | size - 1 (0…3) | ubyte[size] | 无符号(零扩展)四字节整数值,会被解译为要编入 method_handles 区段的索引;表示方法句柄值 |
| VALUE_STRING | 0x17 | size - 1 (0…3) | ubyte[size] | 无符号(零扩展)四字节整数值,会被解译为要编入 string_ids 区段的索引;表示字符串值 |
| VALUE_TYPE | 0x18 | size - 1 (0…3) | ubyte[size] | 无符号(零扩展)四字节整数值,会被解译为要编入 type_ids 区段的索引;表示反射类型/类值 |
| VALUE_FIELD | 0x19 | size - 1 (0…3) | ubyte[size] | 无符号(零扩展)四字节整数值,会被解译为要编入 field_ids 区段的索引;表示反射字段值 |
| VALUE_METHOD | 0x1a | size - 1 (0…3) | ubyte[size] | 无符号(零扩展)四字节整数值,会被解译为要编入 method_ids 区段的索引;表示反射方法值 |
| VALUE_ENUM | 0x1b | size - 1 (0…3) | ubyte[size] | 无符号(零扩展)四字节整数值,会被解译为要编入 field_ids 区段的索引;表示枚举类型常量的值 |
| VALUE_ARRAY | 0x1c | (无;必须为 0) |
encoded_array | 值的数组,采用下文“encoded_array 格式”所指定的格式。value 的大小隐含在编码中。 |
| VALUE_ANNOTATION | 0x1d | (无;必须为 0) |
encoded_annotation | 子注解,采用下文“encoded_annotation 格式”所指定的格式。value 的大小隐含在编码中。 |
| VALUE_NULL | 0x1e | (无;必须为 0) |
(无) | null 引用值 |
| VALUE_BOOLEAN | 0x1f | 布尔值 (0…1) | (无) | 一位值;0 表示 false,1 表示 true。该位在 value_arg 中表示。 |
解析代码如下(该函数在解析DexClassDef的Annotation时才会使用,可先忽略)。
parseEncodedValue 函数 会自动读取单个 encoded_value 并返回解析后的字符串(类型:值 的 键值对 形式)以及 value 占用的真实字节数。
// 读取EncodedValue, 由于大小不固定, 故直接以数组赋值形式取值
void DexFile::getEncodedValue(ubyte* pDest,const ubyte* pValue,int size) {
for(int i=0;i<size;i++) {
pDest[i]=pValue[i];
}
}
// 解析EncodedValue, 返回解析后的字符串以及value真实大小 Todo: 完善解析逻辑,剩余3个分支
std::string DexFile::parseEncodedValue(ubyte* pEncodedValue,size_t& valueRealSize) {
ubyte valueArg = GetValueArg(pEncodedValue[0]);// arg=size-1,值占用的字节数<=对应类型大小,不含头部的单字节
ubyte valueType = GetValueType(pEncodedValue[0]);
// 假如int=0时,占2字节,头1字节,值0占1字节,所以要同时判断arg和type
if(valueArg==0) {
//arg==0时,要确定是arg固定为0的特殊类型还是其他类型
//特殊类型只有1字节头,其他类型是1字节头+1字节数据
bool isSpecialType=false;
switch (valueType) {
case VALUE_BYTE:
case VALUE_ARRAY:
case VALUE_ANNOTATION:
case VALUE_NULL:
case VALUE_BOOLEAN:
isSpecialType=true;
break;
}
if(isSpecialType)
valueRealSize=1;
else
valueRealSize=2;
}
else
valueRealSize=valueArg+2;// 头部1字节+实际大小 size=head+arg+1
int readValueSize=valueArg+1;// 需要读取的字节数
ubyte* pValue=&pEncodedValue[1];
std::string result;
unsigned int index=0;
switch(valueType) {
// 有符号单字节
case VALUE_BYTE: {
char byte=0;
getEncodedValue((ubyte*)&byte,pValue,readValueSize);
result="byte:"+std::format("0x{:x}",byte);
break;
}
// 有符号双字节
case VALUE_SHORT: {
short value_short=0;
getEncodedValue((ubyte*)&value_short,pValue,readValueSize);
result="short:"+std::format("0x{:x}",value_short);
break;
}
// 无符号双字节
case VALUE_CHAR: {
unsigned short value_char=0;
getEncodedValue((ubyte*)&value_char,pValue,readValueSize);
result="char:"+std::format("0x{:x}",value_char);
break;
}
// 有符号4字节
case VALUE_INT: {
int value_int=0;
getEncodedValue((ubyte*)&value_int,pValue,readValueSize);
result="int:"+std::format("0x{:x}",value_int);
break;
}
// 有符号8字节
case VALUE_LONG: {
long long value_long=0;
getEncodedValue((ubyte*)&value_long,pValue,readValueSize);
result="long:"+std::format("0x{:x}",value_long);
break;
}
// 4字节浮点
case VALUE_FLOAT: {
float value_float=0;
getEncodedValue((ubyte*)&value_float,pValue,readValueSize);
result="float:"+std::format("{:f}",value_float);
break;
}
// 8字节浮点
case VALUE_DOUBLE: {
double value_double=0;
getEncodedValue((ubyte*)&value_double,pValue,readValueSize);
result="double:"+std::format("{:f}",value_double);
break;
}
// 无符号4字节索引 指向对应结构
case VALUE_METHOD_TYPE: {
// ProtoId
getEncodedValue((ubyte*)&index,pValue,readValueSize);
result="MethodType:"+std::format("0x{:x}",index)+" "+getProtoIdDataByIndex(index);
break;
}
// todo: 这部分没有定义的成员指向,暂时不知如何解析,参考 https://source.android.com/docs/core/runtime/dex-format?hl=zh-cn#method-handle-item
case VALUE_METHOD_HANDLE: {
// MethodHandles
getEncodedValue((ubyte*)&index,pValue,readValueSize);
result="MethodHandle Index:"+std::format("0x{:x}",index);
break;
}
case VALUE_STRING: {
// StringId
getEncodedValue((ubyte*)&index,pValue,readValueSize);
result="String:"+getStringIdDataByIndex(index);
break;
}
case VALUE_TYPE: {
// TypeId
getEncodedValue((ubyte*)&index,pValue,readValueSize);
result="Type:"+parseString(getTypeIdDataByIndex(index));
break;
}
case VALUE_FIELD: {
// FieldId
getEncodedValue((ubyte*)&index,pValue,readValueSize);
result="Field:"+parseString(getFieldIdDataByIndex(index));
break;
}
case VALUE_METHOD: {
// MethodId
getEncodedValue((ubyte*)&index,pValue,readValueSize);
result="Method:"+parseString(getMethodIdDataByIndex(index));
break;
}
case VALUE_ENUM: {
// FieldId
getEncodedValue((ubyte*)&index,pValue,readValueSize);
result="Enum:"+parseString(getFieldIdDataByIndex(index));
break;
}
// todo encoded_array和encoded_annotation结构,不太容易解析
case VALUE_ARRAY: {
//getEncodedValue((ubyte*)&index,pValue,readValueSize);
// DexEncodedArray encodedArray;//直接解析貌似不正确
// getEncodedValue((ubyte*)&encodedArray,pValue,readValueSize);
// printClassDefStaticValues(encodedArray);
// int sizeLen=0;
// u4 size=myReadUnsignedLeb128(pValue,&sizeLen);
// u1* pValues=pValue+sizeLen;
// printf("EncodedArray contains %d values\n",size);
// unsigned int offset=0;// offset保存前方已访问的结构大小
// for(int i=0;i<size;i++) {
// printf("%s\n",parseEncodedValue(pValues+offset,offset).c_str());
// }
//system("pause");
break;
}
case VALUE_ANNOTATION:
result="Todo......";
break;
case VALUE_NULL:
result="null";
break;
// boolean的值存在value_arg中
case VALUE_BOOLEAN:
result="bool:";
if(valueArg)
result+="true";
else
result+="false";
break;
default:
result="Unknown value type";
}
return result;
}
encoded_array
| 名称 | 格式 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| size | uleb128 | 数组中的元素数量 |
| values | encoded_value[size] | 采用本部分所指定格式的一系列 size encoded_value 字节序列;依序串联。 |
由于 encoded_array.values 数组元素为encoded_value,所以每个元素的大小不固定,不能当作一般的数组解析。
encoded_annotation
该类型主要在 DexClassDef 的 Annotations 部分使用,此处仅做介绍。
| 名称 | 格式 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| type_idx | uleb128 | 注释的类型。这种类型必须是“类”(而非“数组”或“基元”)。 |
| size | uleb128 | 此注解中 name-value 映射的数量 |
| elements | annotation_element[size] | 注解的元素,直接以内嵌形式(不作为偏移量)表示。元素必须按 string_id 索引以升序进行排序。 |
annotation_element
| 名称 | 格式 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| name_idx | uleb128 | 元素名称,表示为要编入 string_ids 区段的索引。该字符串必须符合上文定义的 MemberName 的语法。 |
| value | encoded_value | 元素值 |
上述四者之间的关系如下
annotation_item
└─ encoded_annotation // 注解内容
├─ type_idx // 注解类型
├─ size
└─ annotation_element[]
├─ name (string_idx)
└─ value (encoded_value)
├─ 基本类型
├─ string/type/field/method/enum
├─ encoded_array // 数组
└─ encoded_annotation // 注解嵌套
Dex 整体结构
dex 文件整体结构分为:dex 文件头、索引结构区、data 数据区,示意图如下:
- dex 文件头
- 保存了 dex 文件的基本信息,例如文件大小、dex 头大小、大小端序、索引表的起始地址和大小等;
- 索引结构区
- 这部分保存了字符串表、类型表、方法原型表、域表、方法表等结构;根据这些表和索引可以访问到对应数据;
- data 数据区
- 所有代码和数据存放在该区域。
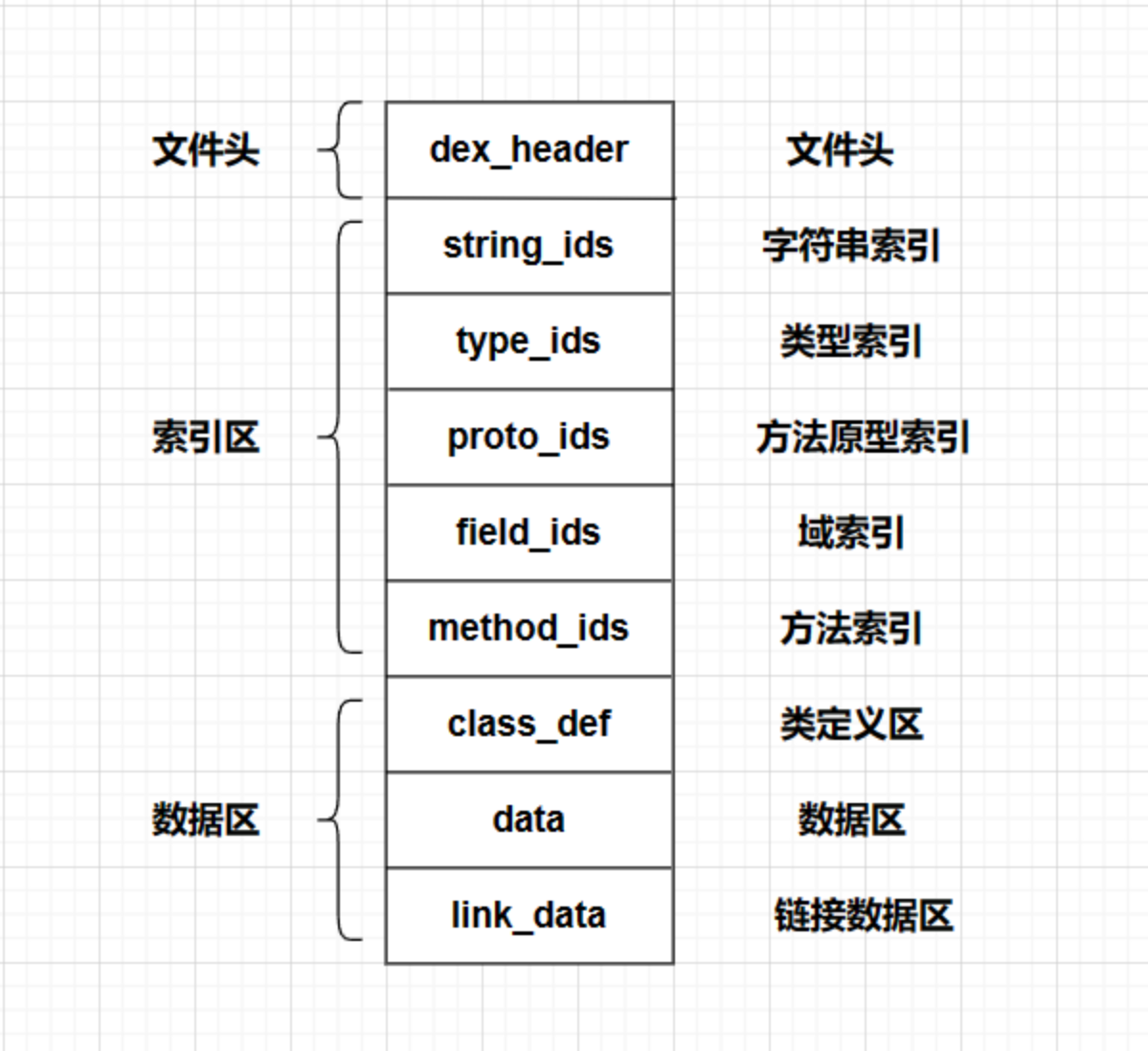
dex 文件结构体的定义在 Android 源码目录 /dalvik/libdex/DexFile.h 中可以找到,其中定义的 dex 文件结构体如下:
struct DexFile {
/* directly-mapped "opt" header */
const DexOptHeader* pOptHeader;
/* pointers to directly-mapped structs and arrays in base DEX */
const DexHeader* pHeader;
const DexStringId* pStringIds;
const DexTypeId* pTypeIds;
const DexFieldId* pFieldIds;
const DexMethodId* pMethodIds;
const DexProtoId* pProtoIds;
const DexClassDef* pClassDefs;
const DexLink* pLinkData;
/*
* These are mapped out of the "auxillary" section, and may not be
* included in the file.
*/
const DexClassLookup* pClassLookup;
const void* pRegisterMapPool; // RegisterMapClassPool
/* points to start of DEX file data */
const u1* baseAddr;
/* track memory overhead for auxillary structures */
int overhead;
/* additional app-specific data structures associated with the DEX */
//void* auxData;
};
为方便使用仅保留部分字段,编写相关函数如下:通过字节 buffer 或文件路径创建 DexFile 类并初始化各个字段
class DexFile {
u1* baseAddr{nullptr};
DexHeader* pHeader{nullptr};
DexStringId* pStringIds{nullptr};
DexTypeId* pTypeIds{nullptr};
DexFieldId* pFieldIds{nullptr};
DexMethodId* pMethodIds{nullptr};
DexProtoId* pProtoIds{nullptr};
DexClassDef* pClassDefs{nullptr};
void initFields(unsigned char *buffer);
}
// Init functions
void DexFile::initFields(unsigned char* buffer) {
if(buffer==nullptr) {
printf("Null pointer provided!\n");
exit(0);
}
baseAddr=buffer;
pHeader=(DexHeader*)baseAddr;
pStringIds=(DexStringId*)(baseAddr+pHeader->stringIdsOff);
pTypeIds=(DexTypeId*)(baseAddr+pHeader->typeIdsOff);
pFieldIds=(DexFieldId*)(baseAddr+pHeader->fieldIdsOff);
pMethodIds=(DexMethodId*)(baseAddr+pHeader->methodIdsOff);
pProtoIds=(DexProtoId*)(baseAddr+pHeader->protoIdsOff);
pClassDefs=(DexClassDef*)(baseAddr+pHeader->classDefsOff);
}
DexFile::DexFile(unsigned char *buffer) {
initFields(buffer);
}
DexFile::DexFile(std::string filePath) {
size_t fileLength=0;
initFields(readFileToBytes(filePath, fileLength));
}
DexFile::~DexFile() {
delete baseAddr;
}
Dex Header
Dex Header 定义如下:
typedef struct DexHeader {
u1 magic[8]; //Dex版本号 dex.035 .035即为版本号
u4 checksum; //adler32检验,如果修改了Dex文件,需要修正这个值,否则会运行不起来
u1 signature[kSHA1DigestLen]; //SHA-1值,Android不检测该值,但如果修改了Dex文件,最好修复该值,再修checksum
u4 fileSize; //整个dex文件的大小
u4 headerSize; //DexHeader结构的大小,固定为0x70
u4 endianTag; //字节序标记,若该字段按小端方式读出来为0x12345678,则整个Dex文件就是小端方式.如果按大端方式读出来为0x12345678,那整个Dex文件就是大端方式
u4 linkSize; //链接段大小
u4 linkOff; //链接段偏移
u4 mapOff; //DexMapList文件偏移
u4 stringIdsSize; //DexStringId个数
u4 stringIdsOff; //DexStringId文件偏移
u4 typeIdsSize; //DexTypeId个数
u4 typeIdsOff; //DexTypeId文件偏移
u4 protoIdsSize; //DexProtoId个数
u4 protoIdsOff; //DexProtoId文件偏移
u4 fieldIdsSize; //DexFieldId个数
u4 fieldIdsOff; //DexFieldId文件偏移
u4 methodIdsSize; //DexMethodId个数
u4 methodIdsOff; //DexMethodId文件偏移
u4 classDefsSize; //DexClassDef个数
u4 classDefsOff; //DexClassDef文件偏移
u4 dataSize; //数据段大小
u4 dataOff; //数据段文件偏移
} DexHeader;
打印 DexHeader
void DexFile::printDexHeader() {
printf("DexHeader:\n");
printf("\tmagic: ");printHexBytes(pHeader->magic,sizeof(pHeader->magic));printf("\n");
printf("\tchecksum: %#x\n",pHeader->checksum);
printf("\tsignature: ");printHexBytes(pHeader->signature,kSHA1DigestLen);printf("\n");
printf("\tFileSize: %#x\n",pHeader->fileSize);
printf("\tHeaderSize: %#x\n",pHeader->headerSize);
printf("\tEndianTag: %#x\n",pHeader->endianTag);
printf("\tLinkOff: %#x\n",pHeader->linkOff);
printf("\tLinkSize: %#x\n",pHeader->linkSize);
printf("\tMapOff: %#x\n",pHeader->mapOff);
printf("\tStringIDs Offset: %#x\n",pHeader->stringIdsOff);
printf("\tNum of StringIDs: %#x\n",pHeader->stringIdsSize);
printf("\tTypeIDs Offset: %#x\n",pHeader->typeIdsOff);
printf("\tNum of TypeIDs: %#x\n",pHeader->typeIdsSize);
printf("\tProtoIDs Offset: %#x\n",pHeader->protoIdsOff);
printf("\tNum of ProtoIDs: %#x\n",pHeader->protoIdsSize);
printf("\tFieldIDs Offset: %#x\n",pHeader->fieldIdsOff);
printf("\tNum of FieldIDs: %#x\n",pHeader->fieldIdsSize);
printf("\tMethodIDs Offset: %#x\n",pHeader->methodIdsOff);
printf("\tNum of MethodIDs: %#x\n",pHeader->methodIdsSize);
printf("\tClassDefs Offset: %#x\n",pHeader->classDefsOff);
printf("\tNum of ClassDefs: %#x\n",pHeader->classDefsSize);
printf("\tData Offset: %#x\n",pHeader->dataOff);
printf("\tSize of Data: %#x\n",pHeader->dataSize);
printf("DexHeader End\n");
}
效果如下: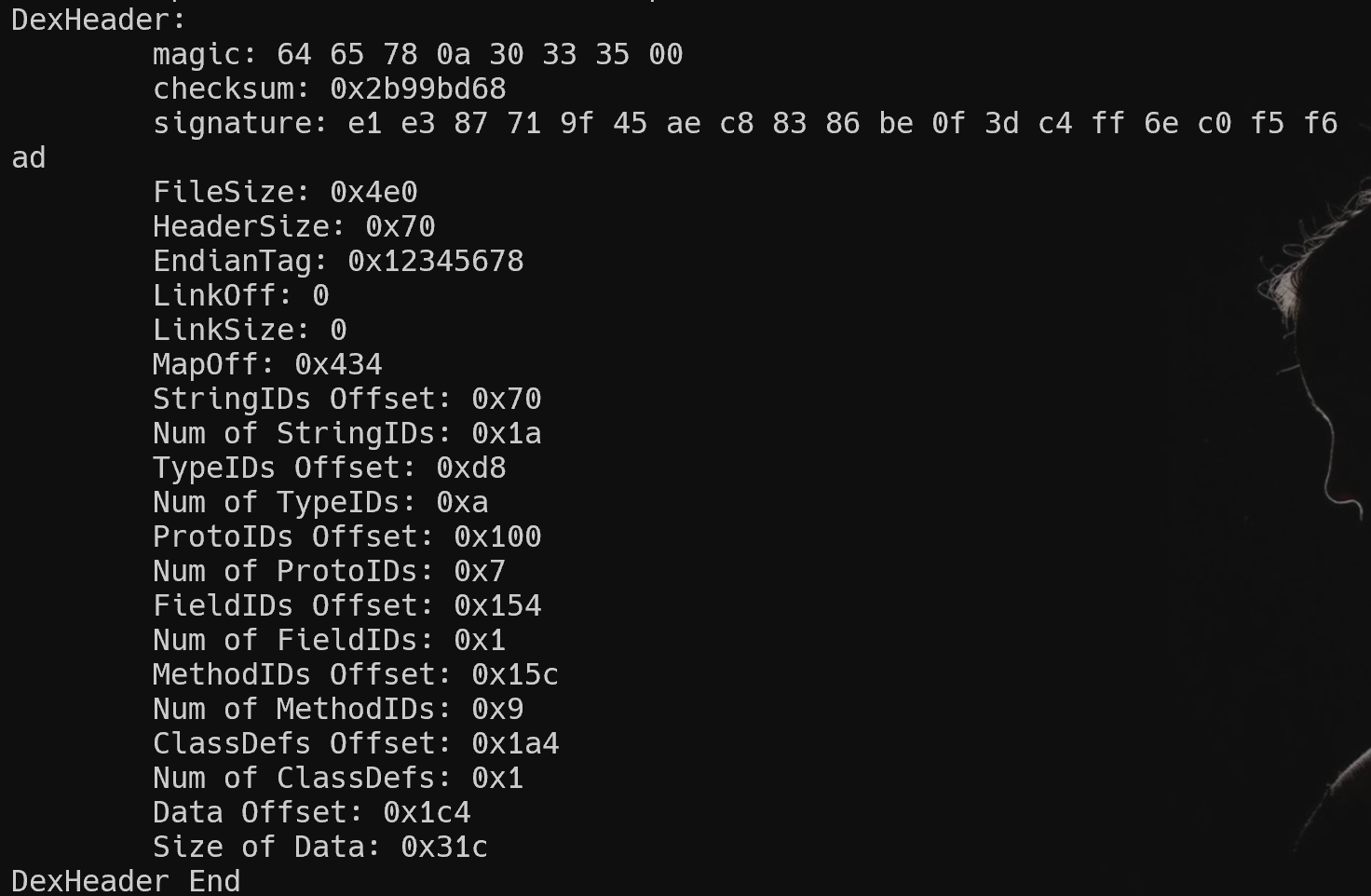
Dex String ID
定义如下
struct DexStringId {
u4 stringDataOff; /* 字符串的文件偏移量 */
};
//伪结构表示如下:
struct string_data_item {
uleb128 utf16_size; //字符串长度
ubyte[] data; //字符串数据
}
注意 dex 文件的字符串采用 MUTF-8 编码,与 UTF-8 区别如下:
- MUTF-8 使用 1~ 3 字节编码;
- 大于 16 位的 Unicode 编码 U + 10000 ~ U + 10ffff 使用 3 字节编码;
- U + 000 采用 2 字节编码;
- 以 0x00 空字符作为字符串结尾。
MUTF-8 字符串头部保存的是字符串长度,是 uleb 128 类型。
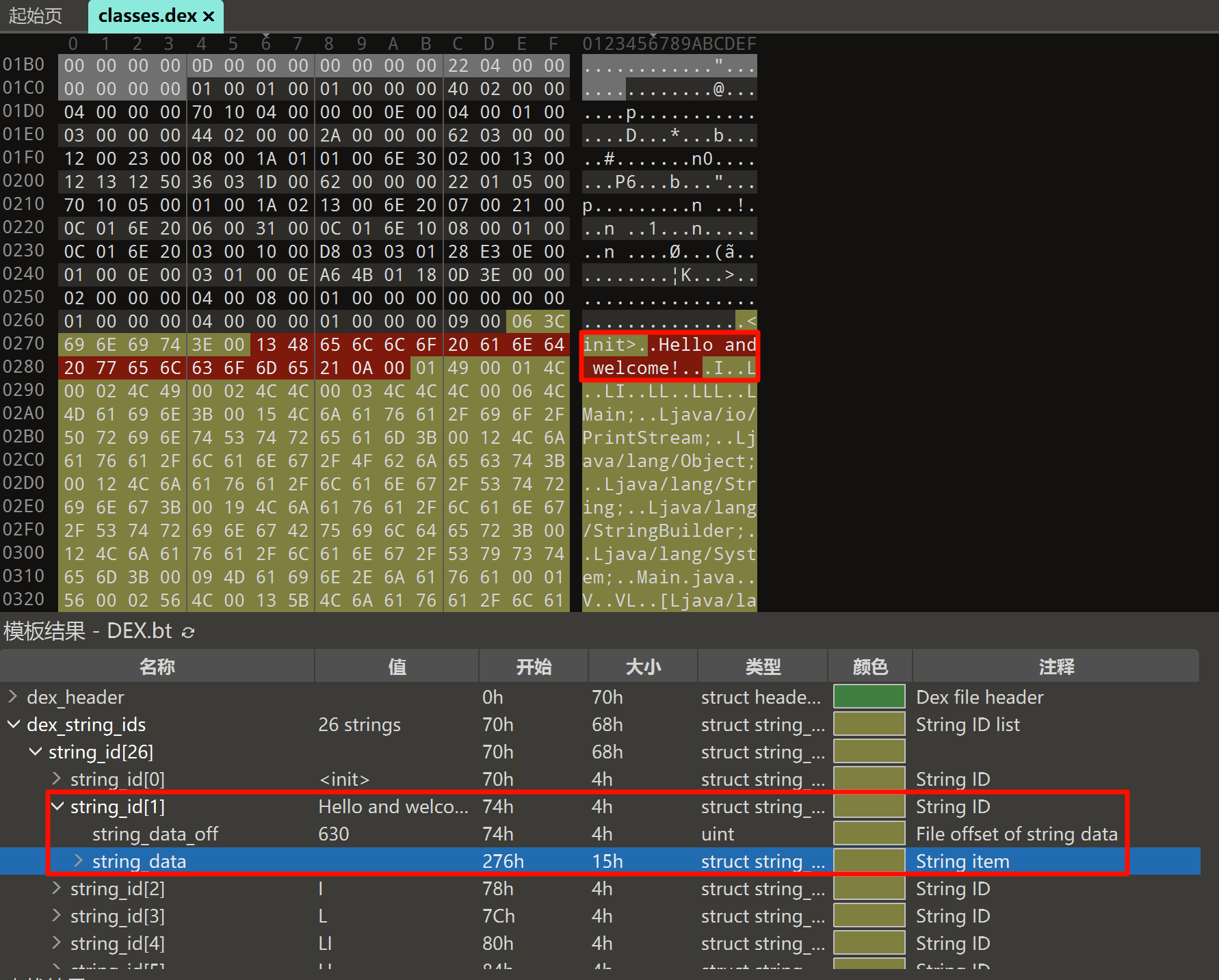
相关函数定义如下,解析 StringId
// StringId functions
// 通过索引获取对应StringId
DexStringId DexFile::getStringIdByIndex(u4 index) {
if(checkIndexIsLegal(index,pHeader->stringIdsSize-1)) {
return pStringIds[index];
}
printf("No such index: %x\n",index);
exit(0);
}
// 解析StringId 获取字符串长度
size_t DexFile::getStringDataLength(DexStringId& stringId) {
const u1* ptr = baseAddr + stringId.stringDataOff;
size_t size=0;
myReadUnsignedLeb128(ptr,&size);
return size;
}
// 解析StringId 获取字符串
std::string DexFile::getStringIdData(const DexStringId& stringId) {
const u1* ptr = baseAddr + stringId.stringDataOff;
while (*(ptr++) > 0x7f);// Skip the uleb128 length.
return (char*)ptr;
}
// 通过索引获取StringId的字符串
std::string DexFile::getStringIdDataByIndex(u4 index) {
if(checkIndexIsLegal(index,pHeader->stringIdsSize-1)) {
return getStringIdData(pStringIds[index]);
}
return nullptr;
}
打印所有 StringId,没有做 MUTF 编码处理,直接打印 ASCII 字符串
void DexFile::printStringIds() {
printf("StringIds:\n");
printf("\tNums\t\tStrings\n");
for(int i=0;i<pHeader->stringIdsSize;i++) {
printf("\t%08x\t%s\n",i,getStringIdDataByIndex(i).c_str());
}
printf("StringIds End\n");
}
效果如下,没有做编码处理
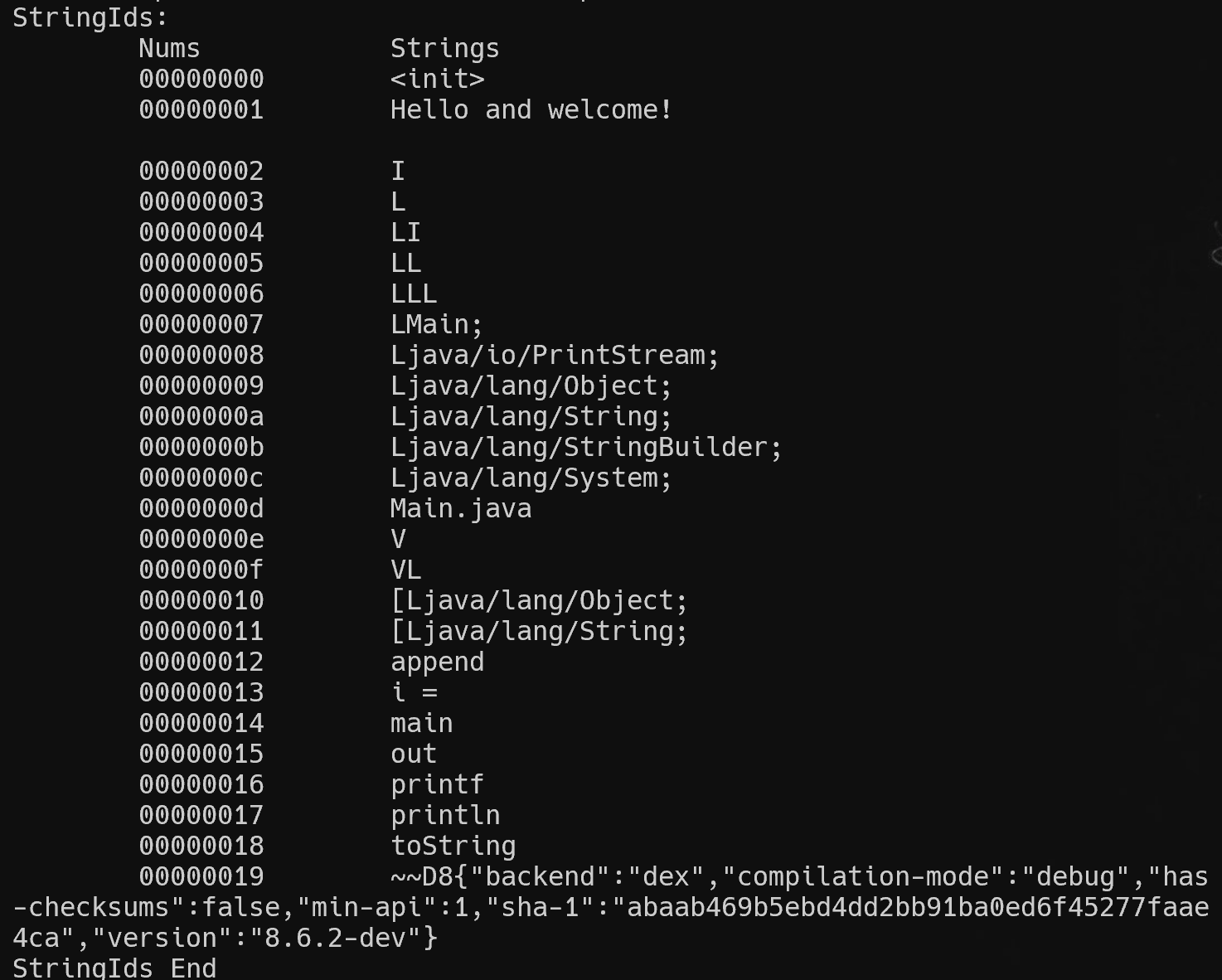
Dex Type ID
定义如下
typedef struct DexTypeId {
u4 descriptorIdx; //指向DexStringId列表的索引
} DexTypeId;
descriptorIdx 为 DexStringID 表的索引,对应字符串表示类的类型。
例如,此处,type_id[4].descriptor_idx = 0xA,而在 dex_string_ids 中,string_id[10] 对应的字符串就是 “Ljava/lang/String;”
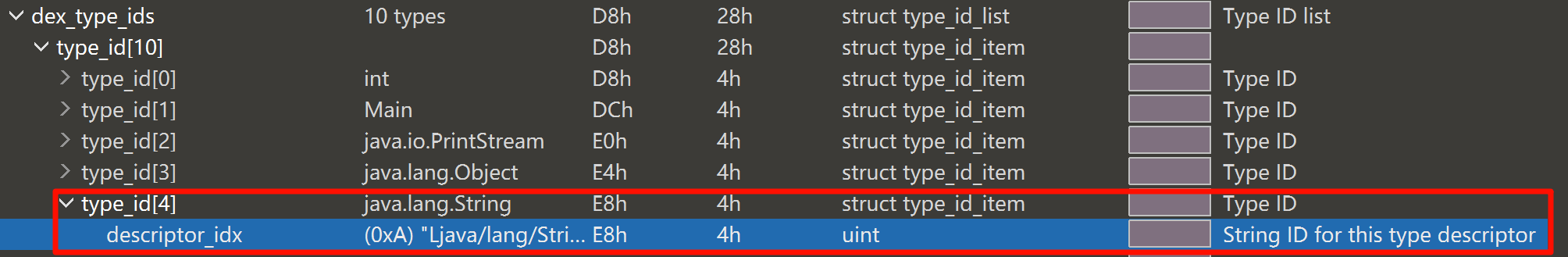
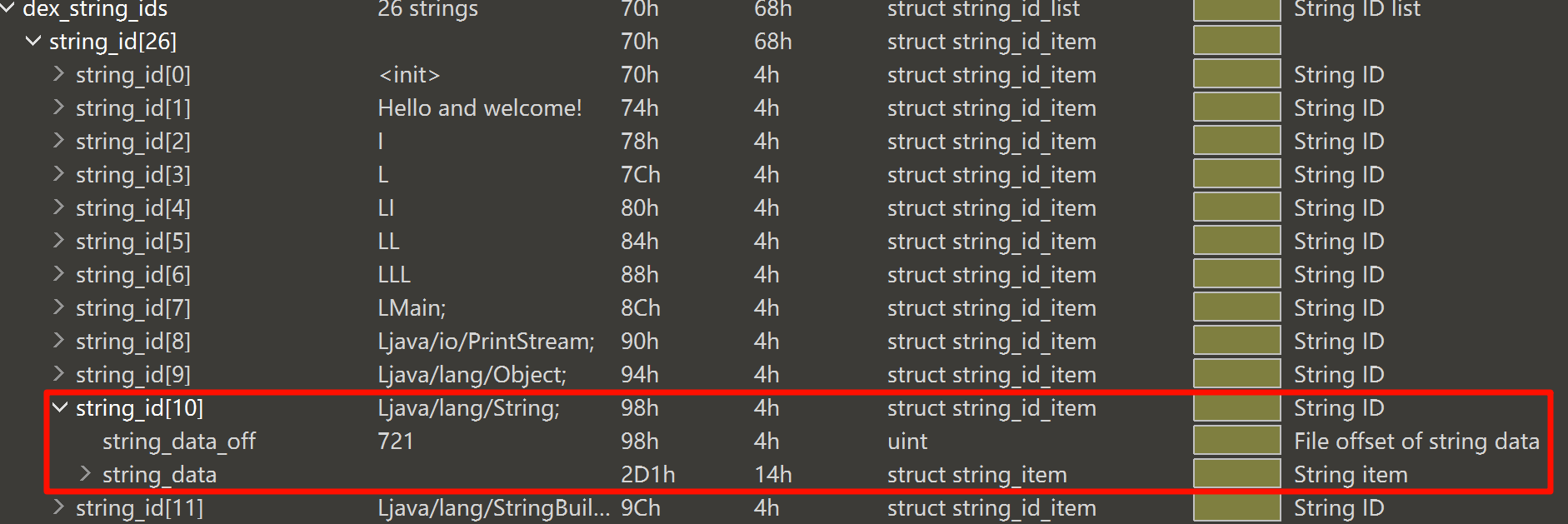
和 StringId 类似,TypeId 的解析代码如下,通过索引获取 StringId 及其对应的字符串。
// TypeId functions
// 通过索引获取对应TypeId
DexTypeId DexFile::getTypeIdByIndex(u4 index) {
if(checkIndexIsLegal(index,pHeader->typeIdsSize-1)) {
return pTypeIds[index];
}
printf("No such index: %x\n",index);
exit(0);
}
// 通过索引获取TypeId对应的字符串
std::string DexFile::getTypeIdDataByIndex(u4 index) {
if(checkIndexIsLegal(index,pHeader->typeIdsSize-1)) {
return getStringIdDataByIndex(pTypeIds[index].descriptorIdx);
}
return nullptr;
}
打印所有 TypeId
void DexFile::printTypeIds() {
printf("TypeIds:\n");
printf("\tNums\t\tTypeIds\n");
for(int i=0;i<pHeader->typeIdsSize;i++) {
printf("\t%08x\t%s\n",i,getTypeIdDataByIndex(i).c_str());
}
printf("TypeIds End\n");
}
效果如下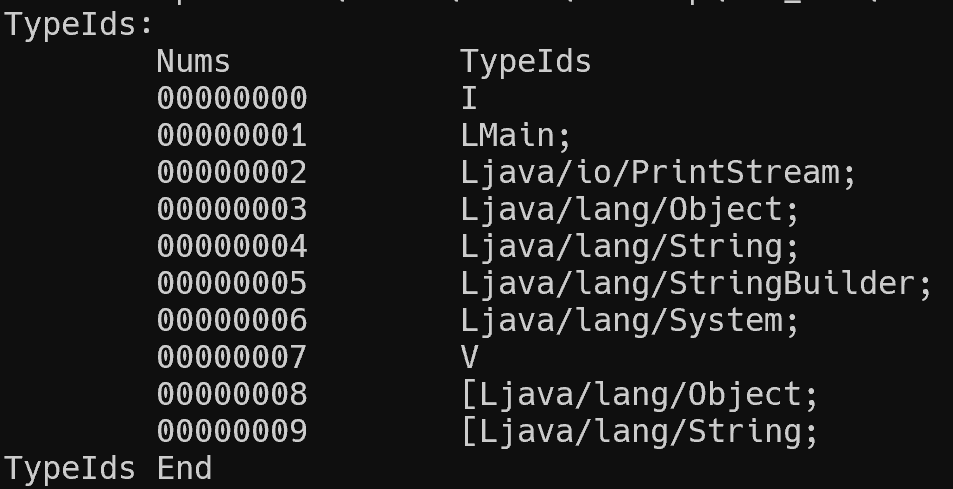
Dex Proto ID
DexProtoId 是 **方法声明(方法签名)**的结构体,保存方法(函数)的返回值类型和参数类型列表,没有函数名,定义如下:
typedef struct DexProtoId {
u4 shortyIdx; //方法声明字符串,指向DexStringId列表的索引
u4 returnTypeIdx; //方法返回类型字符串,指向DexTypeId列表的索引
u4 parametersOff; //方法的参数列表,指向DexTypeList列表的索引
} DexProtoId;
parametersOff 是 DexTypeList 的文件偏移。
DexTypeList
结构定义如下
typedef struct DexTypeList {
u4 size; //DexTypeItem个数, 即参数个数
DexTypeItem list[size]; //DexTypeItem数组, 按从左到右的顺序保存了方法的参数
} DexTypeList;
typedef struct DexTypeItem {
u2 typeIdx; //指向DexTypeId列表的索引
} DexTypeItem;
例如此处 DexProtoID[1]
方法声明 DexStringID[shorty_idx] = “L”
返回类型 DexStringID[DexType[return_type_idx]] = “Ljava/lang/String;”
这里的偏移是 0,所以就没有后续了
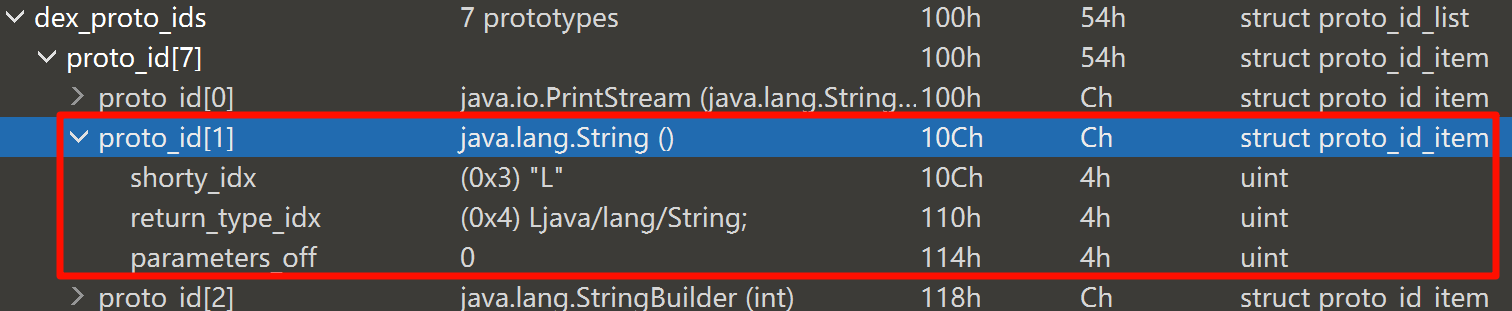
解析代码如下
// ProtoId functions
const DexProtoId DexFile::getProtoIdByIndex(u4 index) {
if(checkIndexIsLegal(index,pHeader->protoIdsSize-1)) {
return pProtoIds[index];
}
illegalIndex(index);
}
std::string DexFile::getProtoIdShorty(const DexProtoId& protoId) {
return getStringIdDataByIndex(protoId.shortyIdx);
}
std::string DexFile::getProtoIdReturnType(const DexProtoId& protoId) {
return getTypeIdDataByIndex(protoId.returnTypeIdx);
}
// 获取ProtoId的参数列表,解析TypeList结构
std::vector<std::string> DexFile::getProtoIdParameters(const DexProtoId& protoId) {
std::vector<std::string> parameters;
//无参数
if(protoId.parametersOff==0) {
return parameters;
}
//解析TypeList结构 获取参数列表
DexTypeList* typeList=(DexTypeList*)(baseAddr+protoId.parametersOff);
for(int i=0;i<typeList->size;i++) {
parameters.push_back(getTypeIdDataByIndex(typeList->list[i].typeIdx));
}
return parameters;
}
// 解析DexProtoId结构体 返回解析后的字符串
std::string DexFile::parseProtoId(const DexProtoId& protoId) {
std::string shorty=getProtoIdShorty(protoId);//c++的string类型会自动遍历const char*字符串并复制
std::string return_type = getProtoIdReturnType(protoId);
std::vector<std::string> parameters=getProtoIdParameters(protoId);
std::string result;
result+=parseString(return_type)+" (";
//解析参数
for(int i=0;i<parameters.size();i++) {
result+=parseString(parameters[i]);
if(i!=parameters.size()-1)//多个参数以,分隔
result+=",";
}
result+=")";
return result;
}
// 通过索引解析ProtoId,返回解析后的对应字符串
std::string DexFile::getProtoIdDataByIndex(u4 index) {
if(checkIndexIsLegal(index,pHeader->protoIdsSize-1)) {
return parseProtoId(getProtoIdByIndex(index));
}
return nullptr;
}
打印所有 ProtoId
void DexFile::printProtoIds() {
printf("ProtoIds:\n");
printf("\tNums\t\tProtoIds\n");
for(int i=0;i<pHeader->protoIdsSize;i++) {
printf("\t%08x\t%s\n",i,getProtoIdDataByIndex(i).c_str());
}
printf("ProtoIds End\n");
}
效果如下
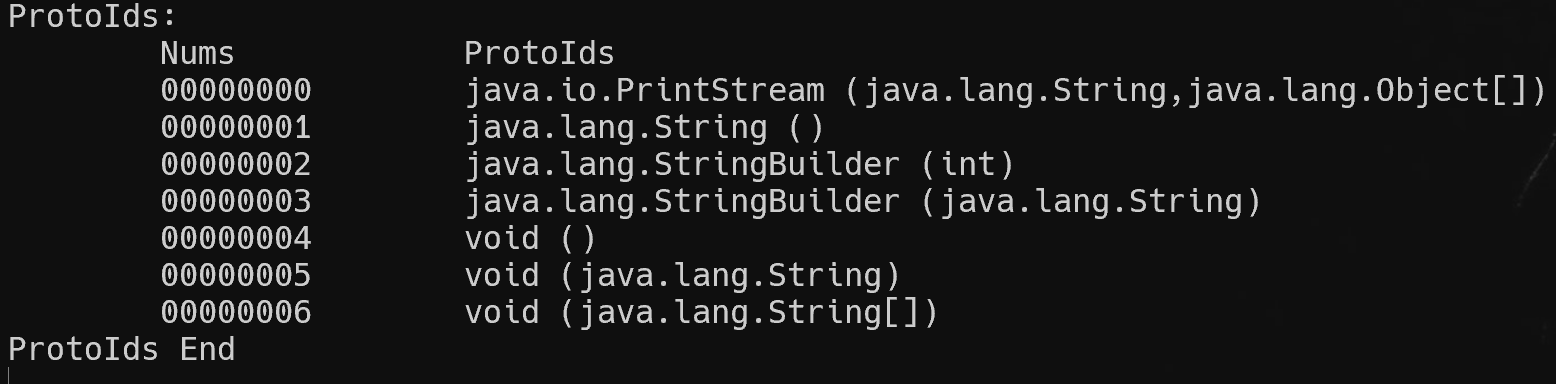
Dex Field ID
DexFiledID 结构体指明了成员变量所在的类,类型以及变量名。
typedef struct DexFieldId {
u2 classIdx; //类的类型,指向DexTypeId列表的索引
u2 typeIdx; //字段类型,指向DexTypeId列表的索引
u4 nameIdx; //字段名,指向DexStringId列表的索引
} DexFieldId;
寻找方法类似,out 是 java.lang.System 类的成员,类型为 java.io.PrintStream。
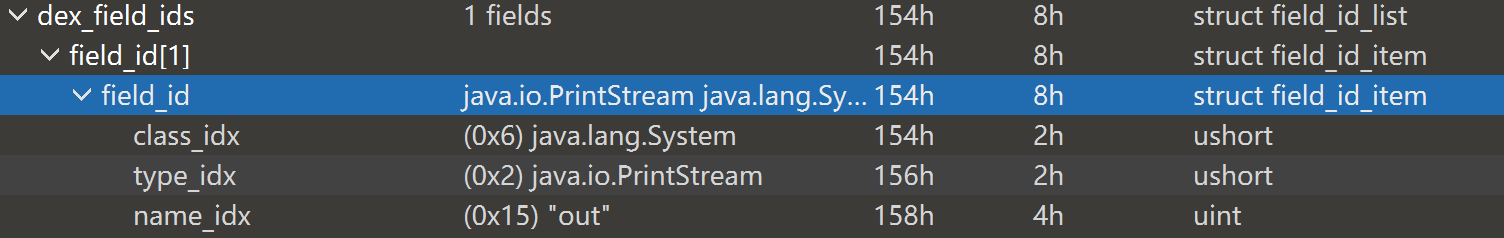
解析代码如下
// FieldId functions
const DexFieldId DexFile::getFieldIdByIndex(u4 index) {
if(checkIndexIsLegal(index,pHeader->fieldIdsSize-1)) {
return pFieldIds[index];
}
illegalIndex(index);
}
// 获取FieldId所在类类名
std::string DexFile::getFieldIdClass(const DexFieldId& fieldId) {
return getTypeIdDataByIndex(fieldId.classIdx);
}
// 获取FieldId类型
std::string DexFile::getFieldIdType(const DexFieldId& fieldId) {
return getTypeIdDataByIndex(fieldId.typeIdx);
}
// 获取FieldId名称
std::string DexFile::getFieldIdName(const DexFieldId& fieldId) {
return getStringIdDataByIndex(fieldId.nameIdx);
}
// 解析DexFieldId结构,字段所在类,类型,名称
std::string DexFile::parseFieldId(const DexFieldId& fieldId) {
std::string fieldClass=getFieldIdClass(fieldId);
std::string fieldType=getFieldIdType(fieldId);
std::string fieldName=getFieldIdName(fieldId);
return parseString(fieldType)+" "+parseString(fieldClass)+"."+fieldName;
}
// 通过索引获取FieldId对应的字符串
std::string DexFile::getFieldIdDataByIndex(u4 index) {
if(checkIndexIsLegal(index,pHeader->fieldIdsSize-1)) {
return parseFieldId(getFieldIdByIndex(index));
}
return nullptr;
}
打印所有 FieldID
void DexFile::printFieldIds() {
printf("FieldIds:\n");
printf("\tNums\t\tFieldIds\n");
for(int i=0;i<pHeader->fieldIdsSize;i++) {
printf("\t%08x\t%s\n",i,getFieldIdDataByIndex(i).c_str());
}
printf("FieldId End\n");
}
效果如下:
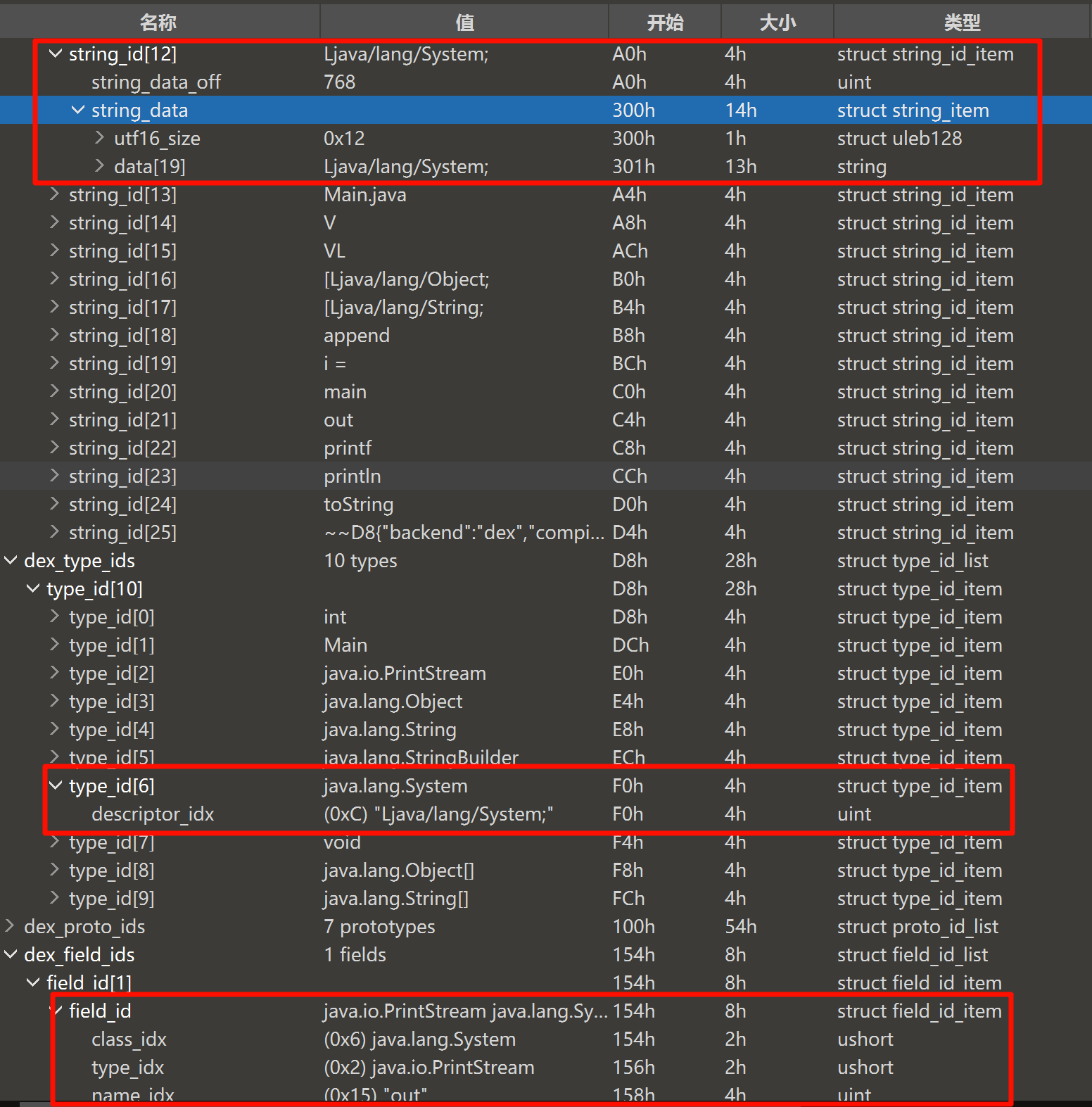
Dex Method ID
DexMethodID 结构体指明了方法所在类、方法声明(签名)以及方法名,即完整的方法声明,
struct DexMethodId {
u2 classIdx; /* 方法的所属的类,指向DexTypeId列表的索引 */
u2 protoIdx; /* 声明类型,指向DexProtoId列表的索引 */
u4 nameIdx; /* 方法名,指向DexStringId列表的索引 */
};
寻找方法,屏幕大小有限,DexMethodID 那里没截完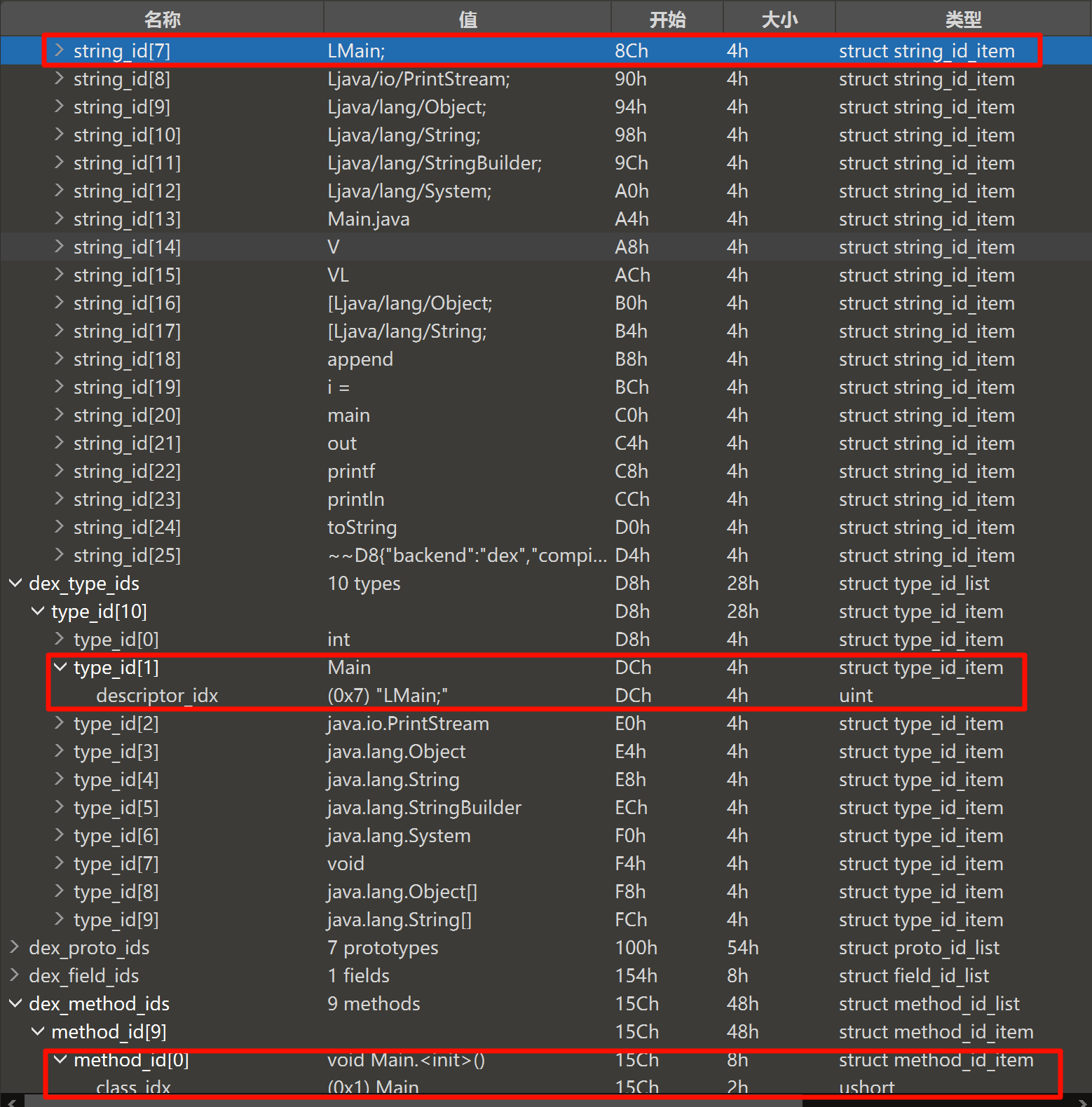
对应解析代码如下:
// MethodId functions
const DexMethodId DexFile::getMethodIdByIndex(u4 index) {
if(checkIndexIsLegal(index,pHeader->methodIdsSize-1)) {
return pMethodIds[index];
}
illegalIndex(index);
}
// 获取MethodId所在类名
std::string DexFile::getMethodIdClass(const DexMethodId& methodId) {
return getTypeIdDataByIndex(methodId.classIdx);
}
// 获取MethodId对应方法签名
std::string DexFile::getMethodIdProto(const DexMethodId& methodId) {
return getProtoIdDataByIndex(methodId.protoIdx);
}
// 获取MethodId对应方法名
std::string DexFile::getMethodIdName(const DexMethodId& methodId) {
return getStringIdDataByIndex(methodId.nameIdx);
}
// 解析DexMethodId结构
std::string DexFile::parseMethodId(const DexMethodId& methodId) {
std::string methodProto=getMethodIdProto(methodId);
//解析class并拼接name
std::string methodFullName=parseString(getMethodIdClass(methodId))+getMethodIdName(methodId);
//拼接proto和class.name
return methodProto.insert(methodProto.find(' ')+1,methodFullName);
}
// 通过索引获取MethodId对应字符串
std::string DexFile::getMethodIdDataByIndex(u4 index) {
if(checkIndexIsLegal(index,pHeader->methodIdsSize-1)) {
return parseMethodId(getMethodIdByIndex(index));
}
return nullptr;
}
打印所有 MethodID
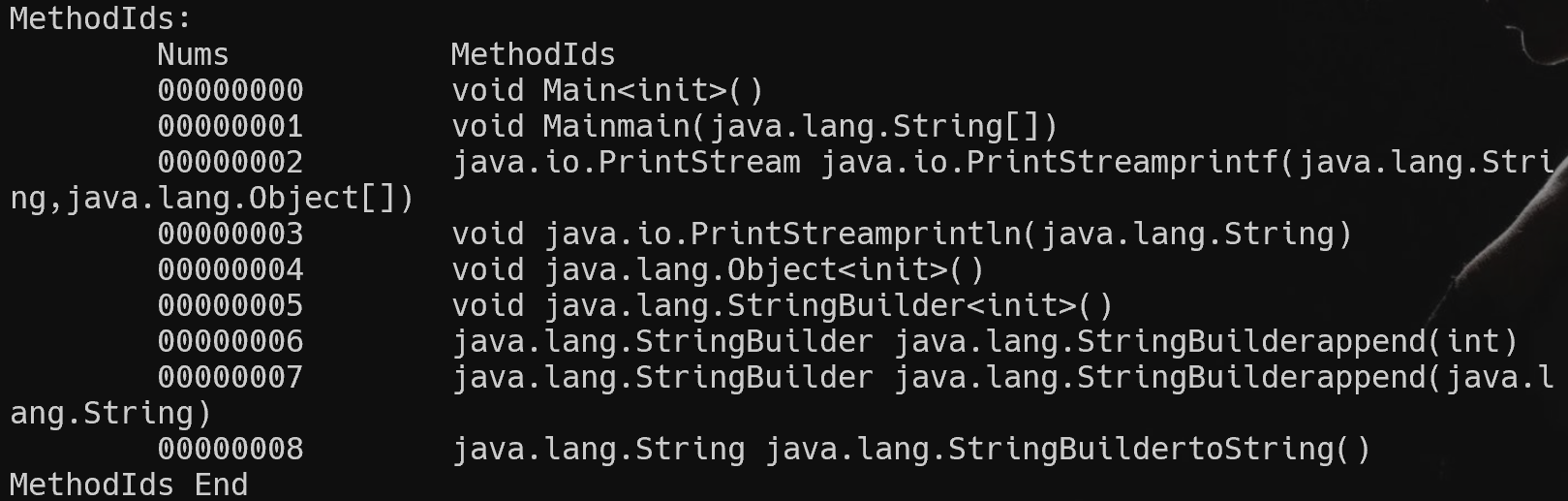
Dex Map List
Dalvik 虚拟机解析 dex 文件后,映射为 DexMapList 的数据结构,该结构由 DexHeader.mapOff 指明位置。
struct DexMapList {
u4 size; /* DexMapItem个数 */
DexMapItem list[1]; /* DexMapItem数组 */
};
struct DexMapItem {
u2 type; /* KDexType开头的类型 */
u2 unused; /* 未使用,用于字节对齐 */
u4 size; /* 类型的个数 */
u4 offset; /* 类型数据的文件偏移 */
};
type 是枚举常量,用于判断类型
/* map item type codes */
enum {
kDexTypeHeaderItem = 0x0000,
kDexTypeStringIdItem = 0x0001,
kDexTypeTypeIdItem = 0x0002,
kDexTypeProtoIdItem = 0x0003,
kDexTypeFieldIdItem = 0x0004,
kDexTypeMethodIdItem = 0x0005,
kDexTypeClassDefItem = 0x0006,
kDexTypeCallSiteIdItem = 0x0007,
kDexTypeMethodHandleItem = 0x0008,
kDexTypeMapList = 0x1000,
kDexTypeTypeList = 0x1001,
kDexTypeAnnotationSetRefList = 0x1002,
kDexTypeAnnotationSetItem = 0x1003,
kDexTypeClassDataItem = 0x2000,
kDexTypeCodeItem = 0x2001,
kDexTypeStringDataItem = 0x2002,
kDexTypeDebugInfoItem = 0x2003,
kDexTypeAnnotationItem = 0x2004,
kDexTypeEncodedArrayItem = 0x2005,
kDexTypeAnnotationsDirectoryItem = 0x2006,
};
size 指定了类型的个数,在 dex 文件中连续存放,offset 是起始地址文件偏移。
例如此处,DexMapList[1] type = TYPE_STRING_ID_ITEM,size = 0x1A,offset = 0x70,和 DexStringID 表正好对应,起始地址,表项数。
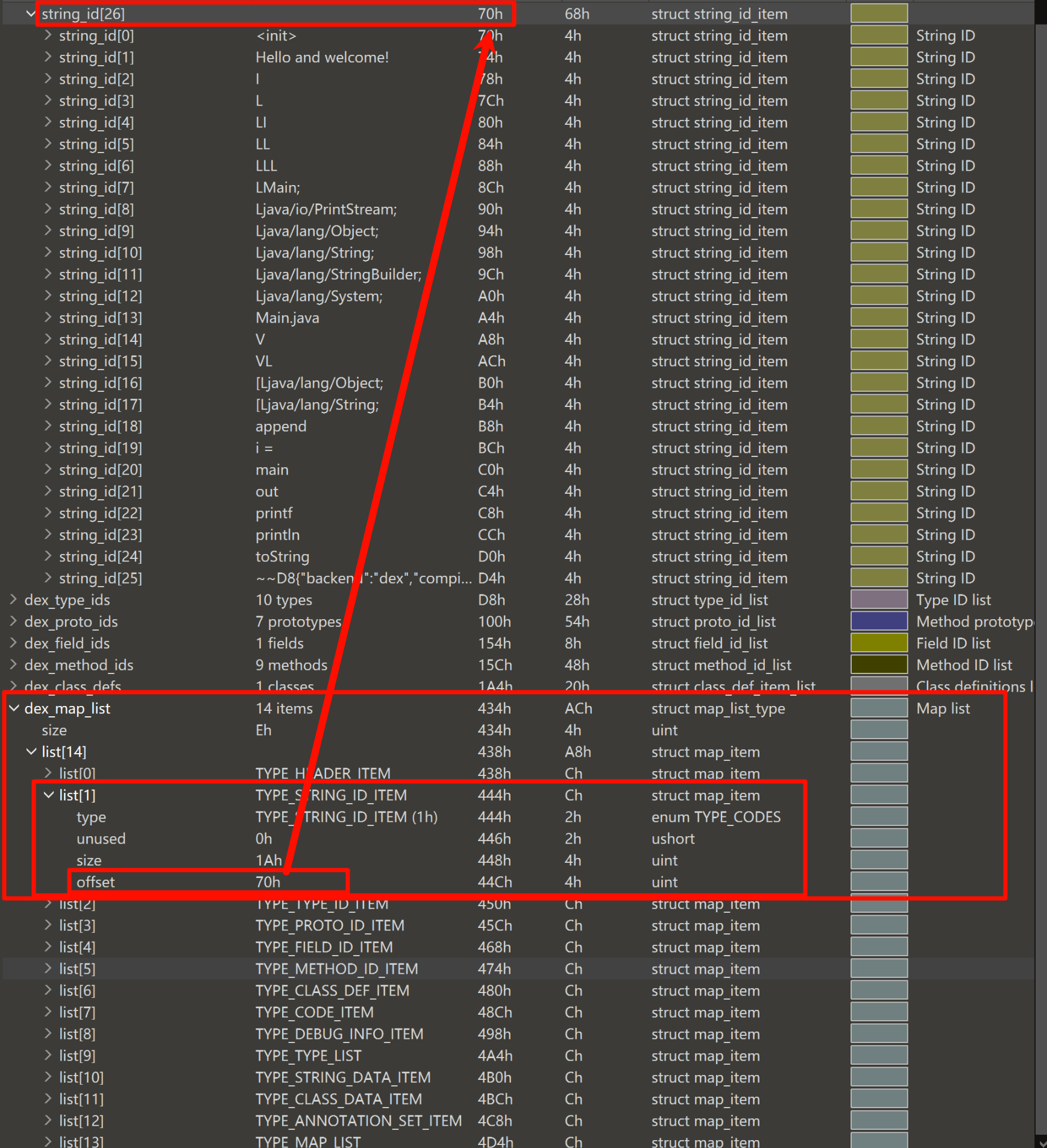
解析代码如下
void DexFile::printMapList() {
static std::map<int, std::string> MapItemTypeToStringMap = {
{kDexTypeHeaderItem, "HeaderItem"},
{kDexTypeStringIdItem, "StringIdItem"},
{kDexTypeTypeIdItem, "TypeIdItem"},
{kDexTypeProtoIdItem, "ProtoIdItem"},
{kDexTypeFieldIdItem, "FieldIdItem"},
{kDexTypeMethodIdItem, "MethodIdItem"},
{kDexTypeClassDefItem, "ClassDefItem"},
{kDexTypeMapList, "MapList"},
{kDexTypeTypeList, "TypeList"},
{kDexTypeAnnotationSetRefList, "AnnotationSetRefList"},
{kDexTypeAnnotationSetItem, "AnnotationSetItem"},
{kDexTypeClassDataItem, "ClassDataItem"},
{kDexTypeCodeItem, "CodeItem"},
{kDexTypeStringDataItem, "StringDataItem"},
{kDexTypeDebugInfoItem, "DebugInfoItem"},
{kDexTypeAnnotationItem, "AnnotationItem"},
{kDexTypeEncodedArrayItem, "EncodedArrayItem"},
{kDexTypeAnnotationsDirectoryItem, "AnnotationsDirectoryItem"}
};
DexMapList* pMapList=(DexMapList*)(baseAddr+pHeader->mapOff);
DexMapItem* pMapItems=pMapList->list;
printf("MapList has %d items, start at: %#x\n",pMapList->size,pHeader->mapOff);
printf("Nums\t\tType\t\t\t\tItemNums\tStartOff\n");
for(int i=0;i<pMapList->size;i++) {
// 解析MapType
auto it=MapItemTypeToStringMap.find(pMapItems[i].type);
std::string mapType;
if(it!= MapItemTypeToStringMap.end())
mapType=it->second;
else mapType="Unknown Type";
printf("%08d\t%-24s\t%08d\t%08x\n",i+1,mapType.c_str(),pMapItems[i].size,pMapItems[i].offset);
}
printf("MapList End\n");
}
打印效果如下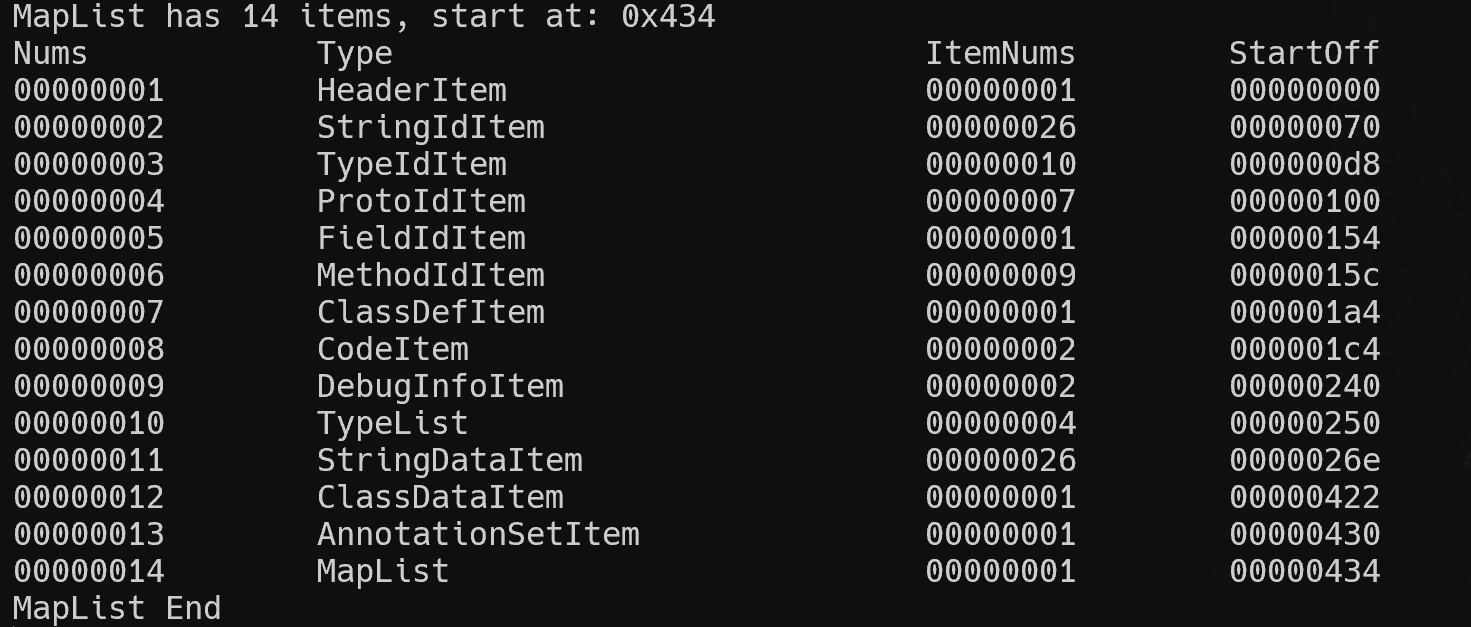
Dex Class Def
该结构较为复杂(这部分相关代码比前文所有结构代码之和都大)。有了对 Dex 文件的基本了解和上面各个结构的基础,才能解析该结构。
DexClassDef 保存了的相关信息,定义如下
struct DexClassDef {
u4 classIdx; /* 类的类型(即全限定类名),指向DexTypeId列表的索引 */
u4 accessFlags; /* 访问标志,以ACC_开头的枚举值,如ACC_PUBLIC(0x1)、ACC_PRIVATE(0x2)*/
u4 superclassIdx; /* 父类类型,指向DexTypeId列表的索引*/
u4 interfacesOff; /* 接口,指向DexTypeList的文件偏移,如果类中不含有接口声明和实现,则值为0 */
u4 sourceFileIdx; /* 类所在源文件的文件名,指向DexStringId列表的索引 */
u4 annotationsOff; /* 注解,指向DexAnnotationsDirectoryItem结构体,根据类型不同会有注解类、注解方法、注解字段与注解参数,如果类中没有注解,则值为0 */
u4 classDataOff; /* 指向DexClassData结构的文件偏移,DexClassData结构是类的数据部分 */
u4 staticValuesOff; /* 指向DexEncodedArray结构的文件偏移,记录类中的静态数据, 没有则为0 */
};
解析代码如下:将 ClassDef 结构划分为 4 部分解析:BasicInfo、Annotations、ClassData、StaticValues,从 classIdx 到 sourceFileIdx 属于 BasicInfo。每部分使用单独的打印函数进行处理。
// 打印所有ClassDef信息
void DexFile::printClassDefs() {
printf("ClassDefs:\n");
for(int i=0;i<pHeader->classDefsSize;i++) {
DexClassDef classDef=pClassDefs[i];
// 1.Basic info
printf("=========================ClassDef %08d=========================\n",i+1);
printClassDefBasicInfo(classDef);
// 2. Annotations
if(classDef.annotationsOff) {
printf("Annotations:\n");
printClassDefAnnotations(*(DexAnnotationsDirectoryItem*)(baseAddr+classDef.annotationsOff));
// 值传递只保留前16字节导致内存访问错,需要引用传递
// DexAnnotationsDirectoryItem annotations_directory_item=*(DexAnnotationsDirectoryItem*)(baseAddr+classDef.annotationsOff);
// parseClassDefAnnotations(annotations_directory_item);
}
else
printf("No Annotations\n");
// 3. ClassData
if(classDef.classDataOff) {
printClassDefClassData(*(DexClassData*)(baseAddr+classDef.classDataOff));
}else
printf("No ClassData\n");
// 4. StaticValues
if(classDef.staticValuesOff) {
printClassDefStaticValues(*(DexEncodedArray*)(baseAddr+classDef.staticValuesOff));
}else
printf("No StaticValues\n");
printf("===================================================================\n");
}
printf("ClassDefs End\n");
}
ClassDefBasicInfo
代码如下
// ClassDef Basic Info functions
// 获取class
std::string DexFile::getClassDefClass(DexClassDef& classDef) {
return parseString(getTypeIdDataByIndex(classDef.classIdx));
}
// 解析权限修饰符
std::string DexFile::parseAccessFlags(u4 accessFlags) {
static std::map<int, std::string> AccessFlagMap = {
{ACC_PUBLIC, "public"},
{ACC_PRIVATE, "private"},
{ACC_PROTECTED, "protected"},
{ACC_STATIC, "static"},
{ACC_FINAL, "final"},
{ACC_SYNCHRONIZED, "synchronized"},
{ACC_SUPER, "super"},
{ACC_VOLATILE, "volatile"},
{ACC_BRIDGE, "bridge"},
{ACC_TRANSIENT, "transient"},
{ACC_VARARGS, "varargs"},
{ACC_NATIVE, "native"},
{ACC_INTERFACE, "interface"},
{ACC_ABSTRACT, "abstract"},
{ACC_STRICT, "strict"},
{ACC_SYNTHETIC, "synthetic"},
{ACC_ANNOTATION, "annotation"},
{ACC_ENUM, "enum"},
{ACC_CONSTRUCTOR, "constructor"},
{ACC_DECLARED_SYNCHRONIZED, "declared_synchronized"}
};
std::string result;
for(int i=0;i<32;i++) {
if(accessFlags & (1 << i)) {
result+=AccessFlagMap[1 << i]+" ";//遍历添加权限控制属性
}
}
if(!result.empty())
result=result.substr(0,result.length()-1);//去除末尾多余空格
return result;
}
// 获取父类
std::string DexFile::getClassDefSuperClass(DexClassDef& classDef) {
return parseString(getTypeIdDataByIndex(classDef.superclassIdx));
}
// 获取接口列表
std::vector<std::string> DexFile::getClassDefInterfaces(DexClassDef& classDef) {
std::vector<std::string> interfaces;
//无参数
if(classDef.interfacesOff==0) {
return interfaces;
}
DexTypeList* typeList=(DexTypeList*)(baseAddr+classDef.interfacesOff);
for(int i=0;i<typeList->size;i++) {
interfaces.push_back(getTypeIdDataByIndex(typeList->list[i].typeIdx));
}
return interfaces;
}
// 获取源文件
std::string DexFile::getClassDefSourceFile(DexClassDef& classDef) {
return getStringIdDataByIndex(classDef.sourceFileIdx);
}
// 打印ClassDef结构的基本信息: 类名 父类 源文件名 接口
void DexFile::printClassDefBasicInfo(DexClassDef& classDef) {
std::string className=getClassDefClass(classDef);
std::string accessFlags=parseAccessFlags(classDef.accessFlags);
std::string superClass=getClassDefSuperClass(classDef);
std::vector<std::string> interfaces=getClassDefInterfaces(classDef);
std::string sourceFile=getClassDefSourceFile(classDef);
// Basic info, class super_class source_file interfaces
printf("Class:\t\t%s\n",combineAccFlagsAndName(accessFlags,className).c_str());
printf("Super Class:\t%s\n",superClass.c_str());
printf("Source File:\t%s\n",sourceFile.c_str());
// print interfaces if have it
if(!interfaces.empty()) {
printf("Interfaces:\nNums\t\tInterface\n");
for(int j=0;j<interfaces.size();j++) {
printf("%08d\t%s\n",j+1,parseString(interfaces[j]).c_str());
}
}else {
printf("No Interfaces\n");
}
}
效果如下(换了一个dex,原本编译的那个太简单,打印出来的内容很少)。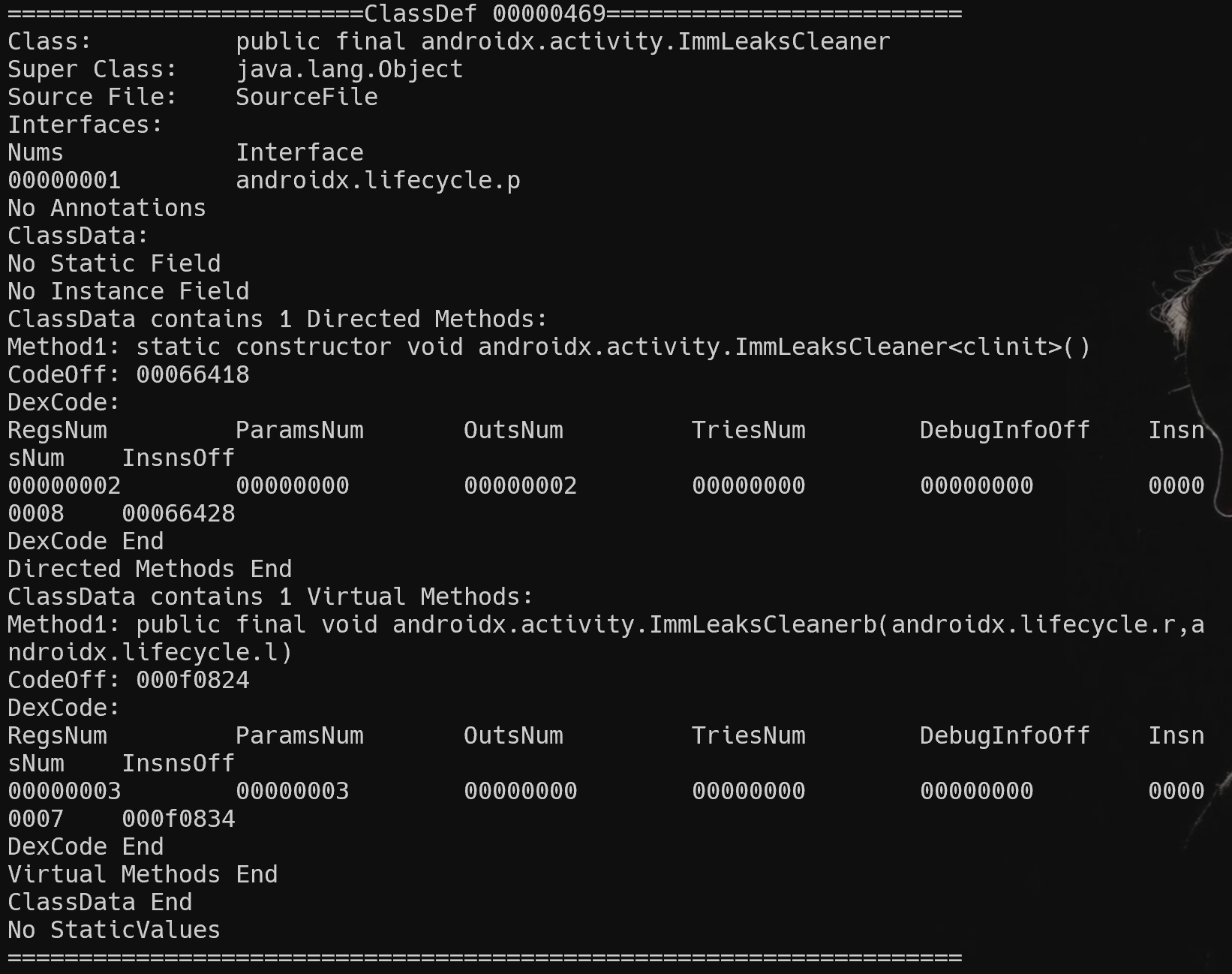
DexAnnotationsDirectoryItem
annotationsOff 指向该结构,用于指向类的所有注解,定义如下。
struct DexAnnotationsDirectoryItem {
u4 classAnnotationsOff; /* 类注解,值为DexAnnotationSetItem的文件偏移量, 为0表示不存在*/
u4 fieldsSize; /* 域注解,值为DexFieldAnnotationsItem的数量 */
u4 methodsSize; /* 方法注解,值为DexMethodAnnotationsItem的数量 */
u4 parametersSize; /* 参数注解。值为DexParameterAnnotationsItem的数量 */
/* 后3结构中存在1个或多个,则在后面追加以下数据,并按顺序排列 */
/* followed by DexFieldAnnotationsItem[fieldsSize] */
/* followed by DexMethodAnnotationsItem[methodsSize] */
/* followed by DexParameterAnnotationsItem[parametersSize] */
};
printClassDefAnnotations 函数用于打印该结构,根据不同注解类型调用不同函数解析。
// 打印ClassDef的所有Annotations
void DexFile::printClassDefAnnotations(DexAnnotationsDirectoryItem& annotationsDirectory) {
//1. 类注解
if(annotationsDirectory.classAnnotationsOff)
printClassAnnotations(*(DexAnnotationSetItem*)(baseAddr+annotationsDirectory.classAnnotationsOff));
else
printf("No Class Annotations\n\n");
//2. 域(字段)注解
if(annotationsDirectory.fieldsSize) {
printFieldAnnotations(
(DexFieldAnnotationsItem*)((uintptr_t)&annotationsDirectory
+sizeof(DexAnnotationsDirectoryItem))
,annotationsDirectory.fieldsSize);
}else
printf("No Field Annotations\n\n");
//3. 方法注解
if(annotationsDirectory.methodsSize) {
printMethodAnnotations(
(DexMethodAnnotationsItem*)
((uintptr_t)&annotationsDirectory
+sizeof(DexAnnotationsDirectoryItem)
+sizeof(DexFieldAnnotationsItem)*annotationsDirectory.fieldsSize)
,annotationsDirectory.methodsSize);
}else {
printf("No Method Annotations\n\n");
}
//4. 参数注解
if(annotationsDirectory.parametersSize) {
printParameterAnnotations(
(DexParameterAnnotationsItem*)((uintptr_t)&annotationsDirectory
+sizeof(DexAnnotationsDirectoryItem)
+sizeof(DexFieldAnnotationsItem)*annotationsDirectory.fieldsSize
+sizeof(DexMethodAnnotationsItem)*annotationsDirectory.methodsSize)
,annotationsDirectory.parametersSize);
}else {
printf("No Parameter Annotations\n\n");
}
}
类注解 DexAnnotationSetItem
struct DexAnnotationSetItem {
u4 size; /* DexAnnotationItem的数量 */
u4 entries[1]; /* entries数组,存储DexAnnotationItem的文件偏移量 */
};
struct DexAnnotationItem {
u1 visibility; /* 此注释的预期可见性 */
u1 annotation[1]; /* encoded_annotation格式的注释内容 */
};
visibility表示注释的可见性,主要有以下几种情况:
| 名称 | 值 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| VISIBILITY_BUILD | 0x00 | 预计仅在构建(例如,在编译其他代码期间)时可见 |
| VISIBILITY_RUNTIME | 0x01 | 预计在运行时可见 |
| VISIBILITY_SYSTEM | 0x02 | 预计在运行时可见,但仅对基本系统(而不是常规用户代码)可见 |
annotation 是采用 encoded_annotation 格式的注释内容,,encoded_annotation格式 如下:
| 名称 | 格式 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| type_idx | uleb128 | 注解的类型,指向DexTypeId列表的索引值 |
| size | uleb128 | 此注解中 name-value 映射的数量 |
| elements | annotation_element[size] | 注解的元素,直接以内嵌形式(不作为偏移量)表示。元素必须按 string_id 索引以升序进行排序。 |
annotation_element元素格式如下:
| 名称 | 格式 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| name_idx | uleb128 | 元素名称,指向DexStringId列表的索引值 |
| value | encoded_value | 元素值 |
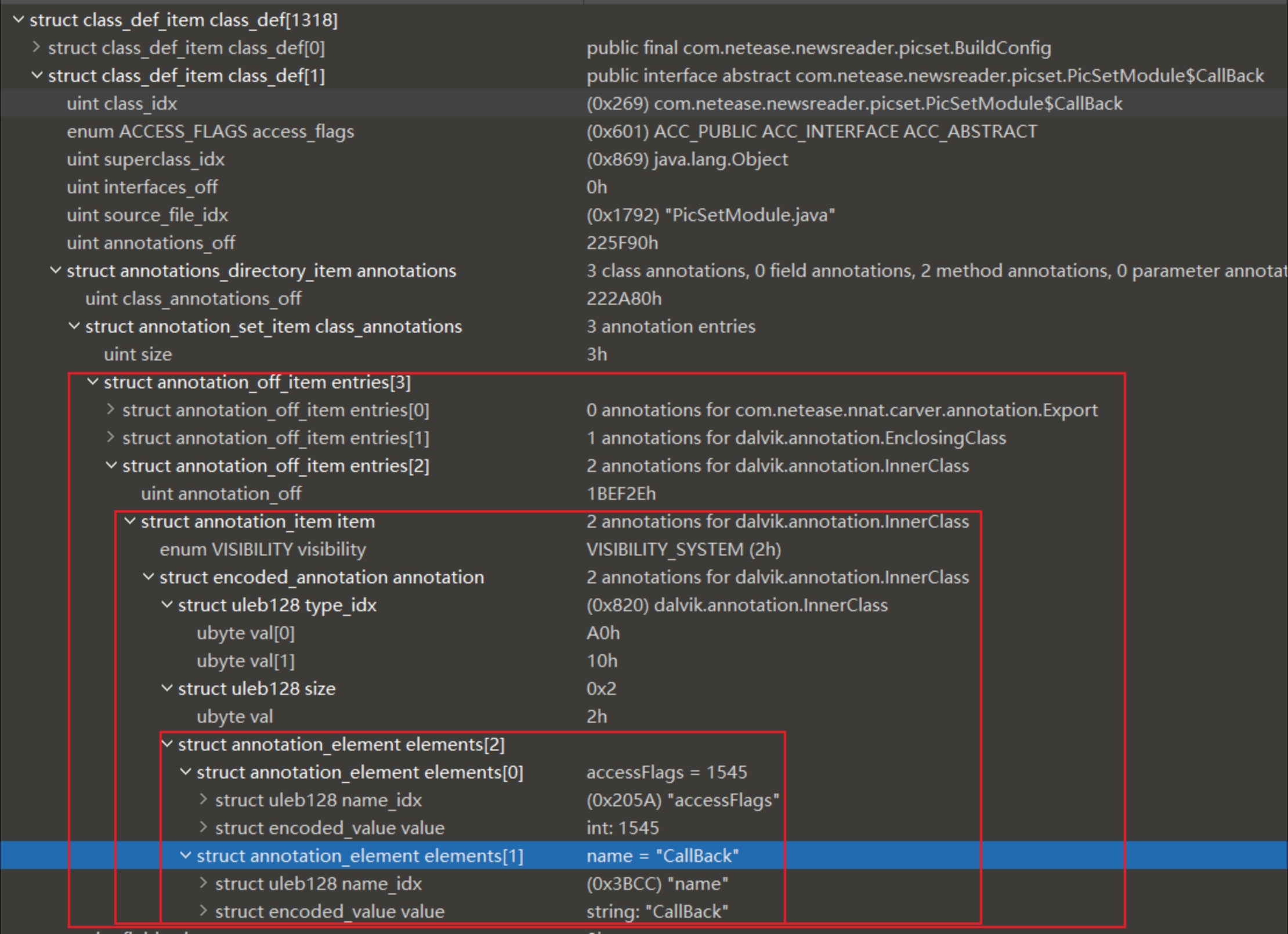
解析代码如下:
// Annotation functions
// 将权限修饰符和方法/类名组合
std::string DexFile::combineAccFlagsAndName(std::string accFlags,std::string name) {
std::string result;
if(accFlags.empty())
result=name;//无权限控制关键字,完整名即可
else
result=accFlags+" "+name;
return result;
}
// 打印DexAnnotationItem结构信息
void DexFile::printAnnotation(DexAnnotationItem& annotationItem) {
std::string visibility;//注解可见性
switch(annotationItem.visibility) {
case kDexVisibilityBuild: visibility="build";break;
case kDexVisibilityRuntime:visibility="runtime";break;
case kDexVisibilitySystem:visibility="system";break;
default:visibility="unknown";
}
// 解析encoded_annotation
u1* pAnnotation=annotationItem.annotation;
size_t typeSize=0,sizeSize=0;
u4 encoded_annotation_type_idx=myReadUnsignedLeb128(pAnnotation,&typeSize);//注解类型偏移
u4 encoded_annotation_size=myReadUnsignedLeb128(pAnnotation+typeSize,&sizeSize);//注解name-value映射数
std::string encoded_annotation_type=parseString(getTypeIdDataByIndex(encoded_annotation_type_idx));
//Size Visibility Type
printf("%08d\t%s\t\t%s\n",encoded_annotation_size,visibility.c_str(),encoded_annotation_type.c_str());
// 解析encoded_annotation.elements
u1* pAnnotationElements=pAnnotation+typeSize+sizeSize;
for(int i=0;i<encoded_annotation_size;i++) {
size_t name_idx_size=0;// name_idx
std::string name=parseString(getStringIdDataByIndex(myReadUnsignedLeb128(pAnnotationElements,&name_idx_size)));
size_t valueSize=0;
std::string value=parseString(parseEncodedValue(pAnnotationElements+name_idx_size,valueSize));
printf("\t%s=%s\n",name.c_str(),value.c_str());
}
}
// 打印DexAnnotationSetItem信息 即多个DexAnnotationItem结构
void DexFile::printAnnotationSet(DexAnnotationSetItem& annotationSet) {
printf("Size\t\tVisibility\tType\n");
//AnnotationSetItem.entries[] 数组保存AnnotationItem结构的文件偏移值
for(int j=0;j<annotationSet.size;j++) {
printAnnotation(*(DexAnnotationItem*)(annotationSet.entries[j]+baseAddr));
}
}
// 打印所有类注解 DexAnnotationSetItem
void DexFile::printClassAnnotations(DexAnnotationSetItem& classAnnotations) {
printf("Class Annotations start at %#llx, contains %d entries\n",(uintptr_t)classAnnotations.entries-(uintptr_t)baseAddr,classAnnotations.size);
printAnnotationSet(classAnnotations);
printf("Class Annotations End\n\n");
}
域注解 DexFieldAnnotationsItem
定义如下
struct DexFieldAnnotationsItem {
u4 fieldIdx; /* 指向DexFieldId列表的索引值 */
u4 annotationsOff; /* DexAnnotationSetItem的文件偏移量 */
};
由于指向 DexAnnotationSetItem 结构,故解析方式和类注解类似。
// 打印所有域注解 DexFieldAnnotationsItem
void DexFile::printFieldAnnotations(DexFieldAnnotationsItem* pFieldAnnotations,u4 fieldsNum) {
printf("Field Annotations start at %#llx, contains %d entries\n",(uintptr_t)pFieldAnnotations-(uintptr_t)baseAddr,fieldsNum);
for(int i=0;i<fieldsNum;i++) {
std::string field=getFieldIdDataByIndex(pFieldAnnotations[i].fieldIdx);
printf("Field%d:\t%s\n",i+1,field.c_str());
printAnnotationSet(*(DexAnnotationSetItem*)(baseAddr+pFieldAnnotations[i].annotationsOff));
}
printf("Field Annotations End\n\n");
}
方法注解 DexMethodAnnotationsItem
定义如下
/*
* Direct-mapped "method_annotations_item".
*/
struct DexMethodAnnotationsItem {
u4 methodIdx; /* 指向DexMethodId列表的索引值 */
u4 annotationsOff; /* DexAnnotationSetItem的文件偏移量 */
};
解析方法类似
// 打印方法注解 DexMethodAnnotationsItem
void DexFile::printMethodAnnotations(DexMethodAnnotationsItem* pMethodAnnotations,u4 methodsNum) {
printf("Method Annotations start at %#llx, contains %d entries\n",(uintptr_t) pMethodAnnotations-(uintptr_t)baseAddr,methodsNum);
for(int i=0;i<methodsNum;i++) {
std::string method=getMethodIdDataByIndex(pMethodAnnotations[i].methodIdx);
printf("Method%d:\t%s\n",i+1,method.c_str());
printAnnotationSet(*(DexAnnotationSetItem*)(baseAddr+ pMethodAnnotations[i].annotationsOff));
}
printf("Method Annotations End\n\n");
}
参数注解 DexParameterAnnotationsItem
定义如下
/*
* Direct-mapped "parameter_annotations_item".
*/
struct DexParameterAnnotationsItem {
u4 methodIdx; /* 指向DexMethodId列表的索引值 */
u4 annotationsOff; /* DexAnotationSetRefList的文件偏移量 */
};
DexAnotationSetRefList 结构体定义如下
/*
* Direct-mapped "annotation_set_ref_list".
*/
struct DexAnnotationSetRefList {
u4 size; /* 列表中元素个数,即DexAnnotationSetRefItem的个数 */
DexAnnotationSetRefItem list[1]; /* 第一个DexAnnotationSetRefItem的内容,非偏移量 */
};
/*
* Direct-mapped "annotation_set_ref_item".
*/
struct DexAnnotationSetRefItem {
u4 annotationsOff; /* DexAnnotationSetItem的偏移量 */
};
解析方法略有不同,代码如下
// 打印DexAnnotationSetRefList
void DexFile::printAnnotationSetRefList(DexAnnotationSetRefList& annotationSetRefList) {
printf("AnnotationSetRefList contains %d AnnotationSetItems\n",annotationSetRefList.size);
// AnnotationSetRefList.list是AnnotationSetRefItem数组
DexAnnotationSetRefItem* pAnnotationSetRefItem=annotationSetRefList.list;
for(int i=0;i<annotationSetRefList.size;i++) {
if(!pAnnotationSetRefItem[i].annotationsOff) {
printf("No This Annotation Set!\n");//可能存在空项
continue;
}
//AnnotationSetRefItem.annotationsOff指向AnnotationSetItem结构
printAnnotationSet(*(DexAnnotationSetItem*)(baseAddr+pAnnotationSetRefItem[i].annotationsOff));
}
printf("AnnotationSetRefList End\n");
}
// 打印参数注解 DexParameterAnnotationsItem
void DexFile::printParameterAnnotations(DexParameterAnnotationsItem* pParameterAnnotations,u4 parametersNum) {
printf("Parameter Annotations start at %#llx, contains %d entries\n",(uintptr_t) pParameterAnnotations-(uintptr_t)baseAddr,parametersNum);
for(int i=0;i<parametersNum;i++) {
std::string method=getMethodIdDataByIndex(pParameterAnnotations[i].methodIdx);
printf("Method%d:\t%s\n",i+1,method.c_str());
// PatameterAnnotationsItem.annotationsOff指向DexAnnotationSetRefList结构,和其他三个不同
printAnnotationSetRefList(*(DexAnnotationSetRefList*)(baseAddr+pParameterAnnotations[i].annotationsOff));
printf("\n");
}
printf("Parameter Annotations End\n\n");
}
DexClassData
定义在 http://androidxref.com/2.3.7/xref/dalvik/libdex/DexClass.h 中。
注意:DexClass.h定义的结构体中,u4类型实际类型为uleb128。
/* expanded form of class_data_item. Note: If a particular item is
* absent (e.g., no static fields), then the corresponding pointer
* is set to NULL. */
typedef struct DexClassData {
DexClassDataHeader header;
DexField* staticFields; //下面4个连续数组,如果对应长度存在才有效
DexField* instanceFields; //按顺序排列
DexMethod* directMethods;
DexMethod* virtualMethods;
} DexClassData;
内部的结构体定义如下:
注意:u4 均为 uleb128,所以这些结构大小不固定,无法通过 sizeof 计算,需要手动计算。
/* expanded form of a class_data_item header */
typedef struct DexClassDataHeader {
u4 staticFieldsSize;
u4 instanceFieldsSize;
u4 directMethodsSize;
u4 virtualMethodsSize;
} DexClassDataHeader;
/* expanded form of encoded_field */
typedef struct DexField {
u4 fieldIdx; /* index to a field_id_item */
u4 accessFlags;
} DexField;
/* expanded form of encoded_method */
typedef struct DexMethod {
u4 methodIdx; /* index to a method_id_item */
u4 accessFlags;
u4 codeOff; /* file offset to a code_item */
} DexMethod;
其中 codeOff 指向 DexCode 结构,定义如下:
/*
* Direct-mapped "code_item".
*
* The "catches" table is used when throwing an exception,
* "debugInfo" is used when displaying an exception stack trace or
* debugging. An offset of zero indicates that there are no entries.
*/
struct DexCode {
u2 registersSize; /* 使用的寄存器个数 */
u2 insSize; /* 参数个数 */
u2 outsSize; /* 调用其他方法时使用的寄存器个数 */
u2 triesSize; /* try_item的个数 */
u4 debugInfoOff; /* 指向调试信息的文件偏移量 */
u4 insnsSize; /* 指令集个数,以2字节为单位 */
u2 insns[1]; /* 指令集,insns 数组中的代码格式由随附文档 Dalvik 字节码指定 */
/* 如果 triesSize 不为零,下面存在*/
/* 两字节填充,使下面的try_item实现4字节对齐 */
/* followed by try_item[triesSize],用于表示代码中捕获异常的位置以及如何对异常进行处理的数组 */
/* followed by uleb128 handlersSize */
/* followed by catch_handler_item[handlersSize],用于表示“捕获类型列表和关联处理程序地址”的列表的字节 */
};
解析代码如下:
// 打印DexCode Todo: 解析DexCode字段
void DexFile::printDexCode(DexCode& dexCode) {
// 打印基本信息
printf("DexCode:\n");
printf("RegsNum\t\tParamsNum\tOutsNum\t\tTriesNum\tDebugInfoOff\tInsnsNum\tInsnsOff\n");
printf("%08d\t%08d\t%08d\t%08d\t%08x\t%08d\t%08x\n",dexCode.registersSize,dexCode.insSize,dexCode.outsSize,dexCode.triesSize,dexCode.debugInfoOff,dexCode.insnsSize,(uintptr_t)dexCode.insns-(uintptr_t)baseAddr);
// 打印
printf("DexCode End\n");
}
// 打印DexClassData的DexField项目 返回对应数组结构的大小
unsigned int DexFile::printClassDataItem(DexField* pFields,u4 fieldsNum) {
u4 prevFieldIndex=0,offset=0;
for(int i=0;i<fieldsNum;i++) {
DexField* pField=(DexField*)((uintptr_t)pFields+offset);
// 注意由于内部元素为uleb128类型,所以DexField大小并不固定,需要计算
size_t fieldIndexSize=0,accessFlagsValueSize=0;
u4 fieldIndex=myReadUnsignedLeb128((u1*)pField,&fieldIndexSize);
u4 accessFlagsValue=myReadUnsignedLeb128((u1*)pField+fieldIndexSize,&accessFlagsValueSize);
std::string fieldName=getFieldIdDataByIndex(prevFieldIndex+fieldIndex);
std::string accessFlags=parseAccessFlags(accessFlagsValue);
printf("Field%d: %s\n",i+1,combineAccFlagsAndName(accessFlags,fieldName).c_str());
prevFieldIndex+=fieldIndex;// 更新前一个filedIndex
offset+=fieldIndexSize+accessFlagsValueSize;//当前数组结构的偏移
}
return offset;//返回当前数组大小
}
// 打印DexClassData的DexMethod项目 返回对应数组结构的大小
unsigned int DexFile::printClassDataItem(DexMethod* pMethods,u4 methodsNum)
{
u4 prevMethodIndex=0,offset=0;
for(int i=0;i<methodsNum;i++) {
DexMethod* pMethod=(DexMethod*)((uintptr_t)pMethods+offset);
size_t methodIndexSize=0,accessFlagsValueSize=0,codeOffSize=0;// 相比DexField多了codeOff,指向DexCode结构
u4 methodIndex=myReadUnsignedLeb128((u1*)pMethod,&methodIndexSize);
u4 accessFlagsValue=myReadUnsignedLeb128((u1*)pMethod+methodIndexSize,&accessFlagsValueSize);
u4 codeOff=myReadUnsignedLeb128((u1*)pMethod+methodIndexSize+accessFlagsValueSize,&codeOffSize);
std::string methodName=getMethodIdDataByIndex(prevMethodIndex+methodIndex);
std::string accessFlags=parseAccessFlags(accessFlagsValue);
printf("Method%d: %s\n",i+1,combineAccFlagsAndName(accessFlags,methodName).c_str());
if(codeOff) {
printf("CodeOff: %08x\n",codeOff);
printDexCode(*(DexCode*)(baseAddr+codeOff));//打印codeOff指向的DexCode
}
else
printf("No DexCode\n");
prevMethodIndex+=methodIndex;
offset+=methodIndexSize+accessFlagsValueSize+codeOffSize;
}
return offset;
}
// 打印DexClassData
void DexFile::printClassDefClassData(DexClassData& classData) {
printf("ClassData:\n");
// 1.解析DexClassDataHeader 获取各uleb128字段保存的长度
const u1* pClassDataHeader=(u1*)&classData.header;
const u1** pPClassDataHeader=&pClassDataHeader;
u4 staticFieldsNum=readUnsignedLeb128(pPClassDataHeader);
u4 instanceFieldsNum=readUnsignedLeb128(pPClassDataHeader);
u4 directMethodsNum=readUnsignedLeb128(pPClassDataHeader);
u4 virtualMethodsNum=readUnsignedLeb128(pPClassDataHeader);
// pointer指向DexClassDataHeader后方第一个字节(即4个数组的内容),用于后续计算
uintptr_t pointer=((uintptr_t)&classData+unsignedLeb128Size(staticFieldsNum)
+unsignedLeb128Size(instanceFieldsNum)
+unsignedLeb128Size(directMethodsNum)
+unsignedLeb128Size(virtualMethodsNum));
// 2. 解析各个字段(判断是否存在对应字段)
// 注意:
// 1. fieldIdx和accessFlags均为uleb128类型
// 2. 数组首个fieldIndex和methodIndex是正确的,后续index是相对前一个index的偏移值(大部分为1)
// 3. 由于各个结构大小不固定,但是四个数组是连续的,所以要使用offset记录前方数据的大小
unsigned int offset=0;
if(staticFieldsNum) {
printf("ClassData contains %d Static Fields:\n",staticFieldsNum);
offset+=printClassDataItem((DexField*)(pointer+offset),staticFieldsNum);
printf("Static Fields End\n");
}
else {
printf("No Static Field\n");
}
if(instanceFieldsNum) {
printf("ClassData contains %d Instance Fields:\n",instanceFieldsNum);
offset+=printClassDataItem((DexField*)(pointer+offset),staticFieldsNum);
printf("Instance Fields End\n");
}
else {
printf("No Instance Field\n");
}
if(directMethodsNum) {
printf("ClassData contains %d Directed Methods:\n",directMethodsNum);
offset+=printClassDataItem((DexMethod*)(pointer+offset),directMethodsNum);
printf("Directed Methods End\n");
}
else {
printf("No Directed Method\n");
}
if(virtualMethodsNum) {
printf("ClassData contains %d Virtual Methods:\n",virtualMethodsNum);
offset+=printClassDataItem((DexMethod*)(pointer+offset),virtualMethodsNum);
printf("Virtual Methods End\n");
}
else {
printf("No Virtual Method\n");
}
printf("ClassData End\n");
}
DexEncodedArray
定义如下
struct DexEncodedArray {
u1 array[1]; //encoded_array格式的数据
};
encoded_array 格式定义如下:
| 名称 | 格式 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| size | uleb128 | 表示数组中的元素数量 |
| values | encoded_value[size] | 采用encoded_value编码的数据 |
解析代码如下
// 打印StaticValues 实际为DexEncodedArray结构
void DexFile::printClassDefStaticValues(DexEncodedArray& encodedArray) {
size_t sizeLen=0;
u4 size=myReadUnsignedLeb128((u1*)&encodedArray,&sizeLen);
u1* pValues=(u1*)&encodedArray+sizeLen;
printf("StaticValues contains %d values\n",size);
size_t offset=0,readSize=0;// offset保存前方已访问的结构大小,readSize为单次读取的大小
for(int i=0;i<size;i++) {
printf("%s\n",parseEncodedValue(pValues+offset,readSize).c_str());
offset+=readSize;
}
printf("StaticValues End\n");
}
Android 系统可执行文件
从 JVM 到 Dalvik 再到 ART
- JVM 是 Java语言的虚拟机,运行 .class 文件;
- Dalvik 是 Google 设计的用于 Android 平台的虚拟机,运行 .dex 文件;JVM 基于栈,DVM 基于寄存器,可以做到更好的提前优化,并且运行速度更快。
- Android 4.4 首次提出 ART 虚拟机,在 Android 5.0 后弃用 Dalvik,默认使用ART,运行 oat 文件。DVM 应用运行时,字节码需要通过即时编译器 JIT 转换为机器码运行;ART 则在应用第一次安装时,预先将字节码编译为机器码,该过程称之为预编译(AOT Ahead of time)。
DEX
- .java文件经 javac 编译后生成 .class 文件,再通过 dx/d8 生成 .dex 文件;
- Dalvik 虚拟机运行 .dex 文件,一个 apk 包内可能含有多个 dex 文件。
ODEX
Android5.0前,使用 Dalvik 虚拟机,ODEX 是 Dalvik 对 Dex 文件优化后的产物, 通常存放在 /data/dalvik-cache目录下。运行程序时直接加载 ODEX 文件,避免重复验证和优化;Android 5.0后,使用 ART 虚拟机,.ODEX 实际上是OAT 文件(ART定制的ELF文件)。
OAT
- OAT 文件是 Android4.4 中引入的,,Android5.0 后,系统默认虚拟机为ART;
- OAT 文件即是 ART 虚拟机对 Dex 优化后的产物,是Android 定制的 ELF 文件;
- OAT 文件结构随 Android 版本变化而变化,没有向后兼容性。
VDEX
VDEX 文件在 Android 8.0 后引入,不是 Android 系统的可执行文件。
Android 8.0 后,dex2oat 将 class.dex 优化生成 2 个文件: OAT 文件(.odex)和 VDEX 文件(.vdex)。
- .odex 文件包含了本机代码的 OAT 文件;
- .vdex 文件包含了原始的 dex 文件副本;
- vdex 文件同 oat 文件一样,随系统版本变化,且没有向后兼容性。
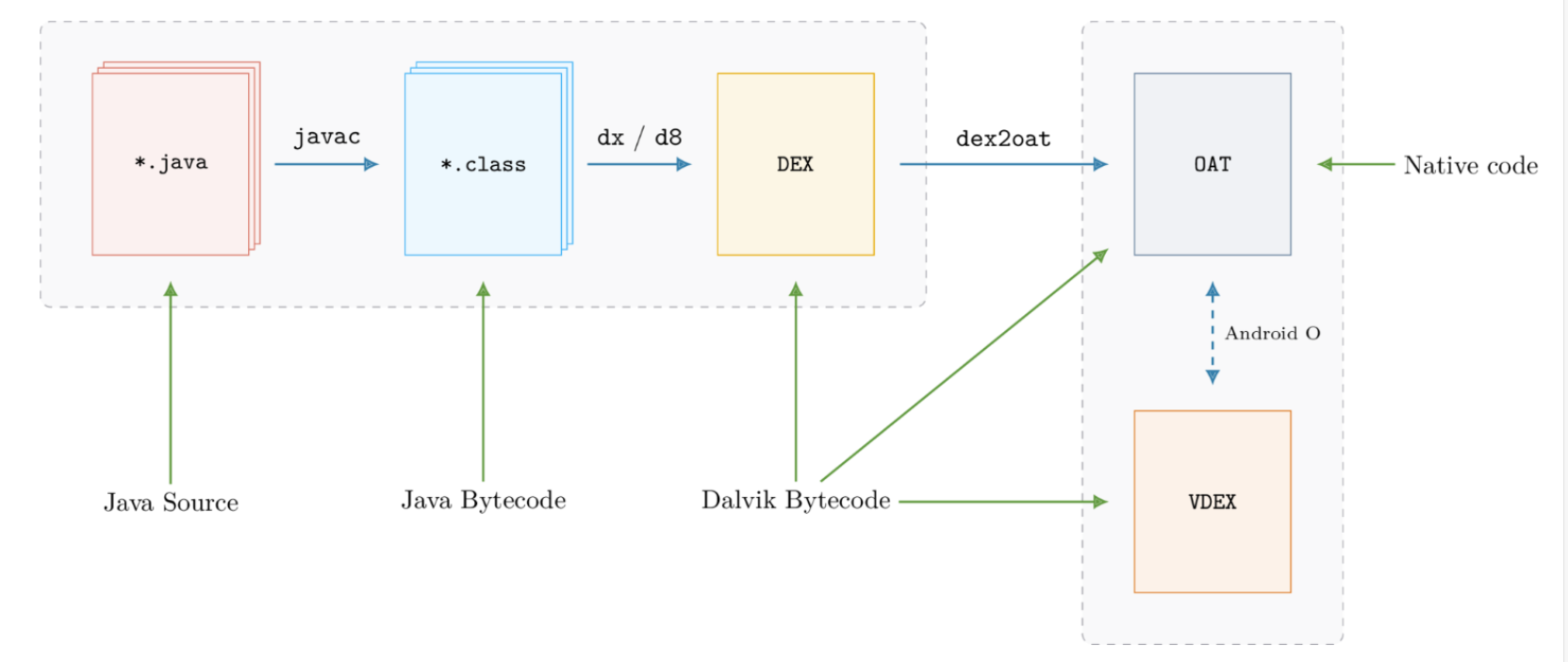
ART
.art 文件是一种 ELF 可执行文件,借助 odex 文件优化生成,记录应用启动的热点函数相关地址,便于寻址加速。
.art文件结构随 Android 版本变化,无向后兼容性。
转载请注明来源,欢迎对文章中的引用来源进行考证,欢迎指出任何有错误或不够清晰的表达。可以在下面评论区评论,也可以邮件至 1621925986@qq.com

